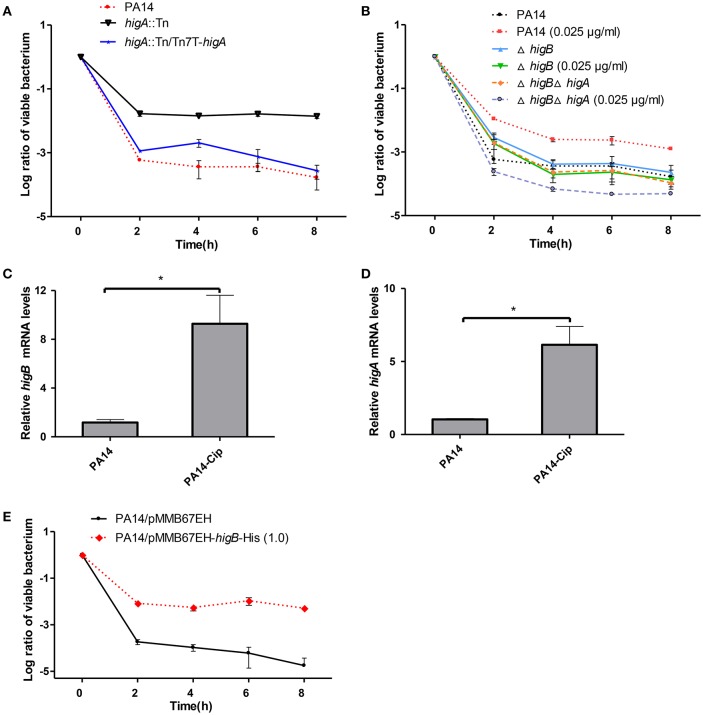
Figure 2.
Role of HigA-HigB in persister formation. (A) Wild type PA14, a higA::Tn mutant and a complemented strain were treated with 0.25 μg/ml ciprofloxacin. At indicated time points the survival rates were determined by plating assay. (B) Wild type PA14, the ΔhigA and ΔhigAΔhigB mutants were cultured in the presence or absence of 0.025 μg/ml ciprofloxacin for 2 h and then treated with 0.25 μg/ml ciprofloxacin. The survival rates were determined by plating assay. (C,D) Wild type PA14 was treated with 0.025 μg/ml ciprofloxacin for 2 h and the mRNA levels of higB or higA were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. Error bars represent the standard error. *p < 0.05, by Student's t-test. (E) Wild type PA14 carrying a Ptac driven higB gene or the empty vector were cultured with 1 mM IPTG for 2 h, followed by treatment with 0.25 μg/ml ciprofloxacin. The survival rates were determined by plating. Error bars represent the standard errors. The graphs are representatives of three independent experiments.