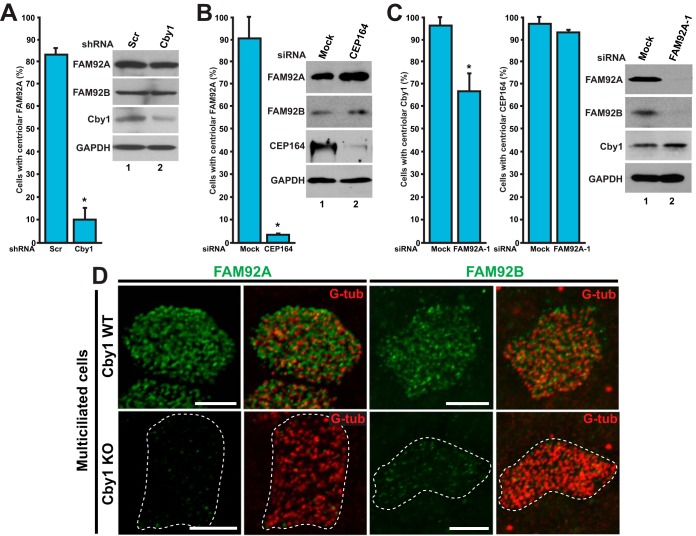
FIG 6.
Cby1 is required for proper targeting of FAM92A and -92B to centrioles/basal bodies. (A) U2OS cells were transfected with an expression vector for either Cby1 shRNA or control scrambled shRNA (Scr) and immunostained for Cby1 and FAM92A to examine the centriolar recruitment of FAM92A. Cby1-positive cells for scrambled shRNA-transfected controls and Cby1-negative cells for Cby1 shRNA-transfected samples were counted in three independent experiments (a total of over 500 cells per shRNA). Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. *, P < 0.05. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting as indicated. GAPDH served as a loading control. (B) U2OS cells were transfected with CEP164 siRNA or mock transfected and immunostained for FAM92A and G-tub to assess the effects of CEP164 depletion on FAM92A localization at centrioles. At least 200 cells were counted in three independent experiments under each condition. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. *, P < 0.05. (C) U2OS cells were transfected with FAM92A siRNA-1 or mock transfected and immunostained for Cby1 and FAM92A or CEP164 and G-tub to examine whether FAM92A depletion influences the centriolar recruitment of Cby1 and CEP164. For Cby1, FAM92A-positive cells for mock-transfected controls and FAM92A-negative cells for FAM92A siRNA-1-transfected samples were counted in 15 independent experiments (a total of over 2,000 cells under each condition). For CEP164, at least 200 cells were counted in three independent experiments. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. *, P < 0.05. Note that FAM92A depletion substantially reduced FAM92B protein levels. (D) Cby1-WT and -KO MTECs at ALI day 14 were colabeled for FAM92A or -92B and the basal body marker G-tub. Bars, 5 μm.