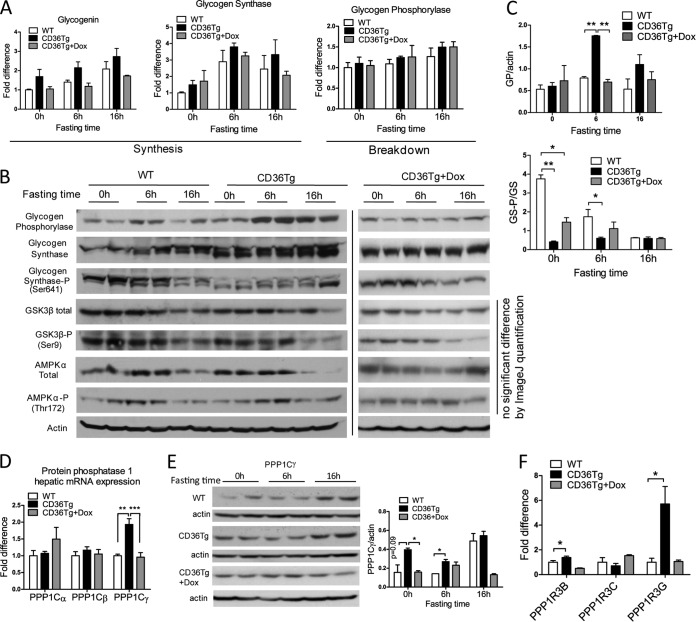
FIG 6.
Molecular mechanism for promoting glycogen synthesis by CD36. WT, CD36Tg, and CD36Tg-plus-Dox mice maintained on a chow diet were subjected to 6 h and 16 h of fasting. (A) The hepatic mRNA expression of glycogenin, GS, and glycogen phosphorylase genes was measured by real-time PCR. (B) The protein expression of GP, total and Ser641-phosphorylated GS, total and Ser9-phosphorylated GSK3β, and total and phosphorylated AMPKα was measured by Western blotting. (C) Densitometric quantification of GP and GS-P/GS expression. (D) mRNA expression of PP1 catalytic subunits (PPP1Cs). (E) Protein expression of PPP1Cγ as measured by Western blotting. Shown on the right are densitometric quantifications of the blots. (F) mRNA expression of PPP1R3B, PPP1R3C, and PPP1R3G regulatory glycogen targeting subunits of PP1. n = 4 for all groups. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., statistically not significant. The data are presented as means and SEM.