Figure 1.
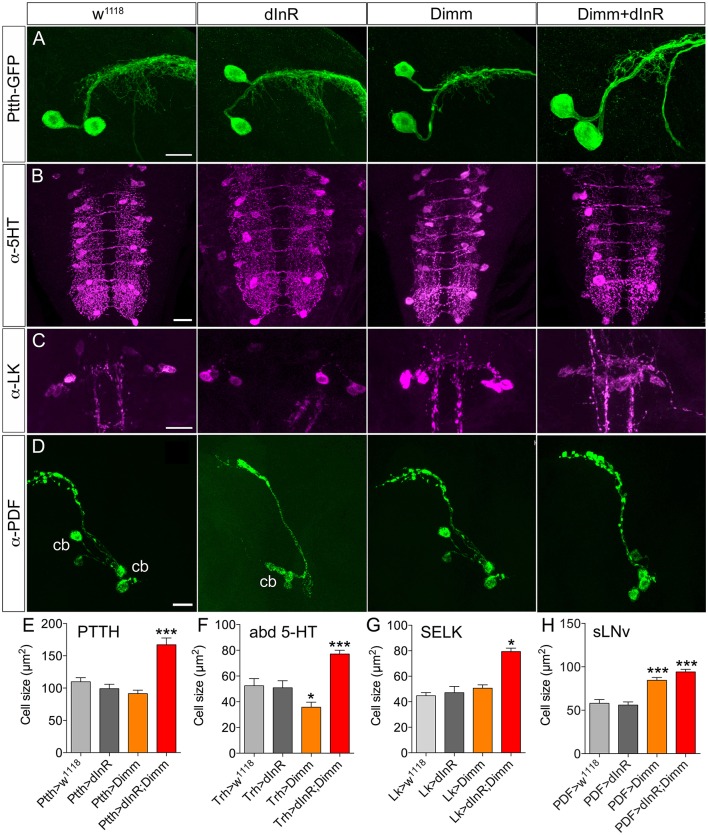
Growth effects of ectopic expression of Dimm and dInR in Dimm-negative neurons in the third instar stage larva depend on neuron type. (A) The Ptth-Gal4 driven GFP displays two PTTH neurons in each hemisphere of the larval brain. Expression dInR or Dimm alone has no effect on cell body size of PTTH neurons, whereas expression of Dimm/dInR triggers growth. (B) A Trh-Gal4 is used to drive Dimm and/or dInR expression in serotonin producing neurons. The cell body size of serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the ventral nerve cord (VNC; abd 5-HT) decreases after Dimm expression, but increases after Dimm/dInR. (C) Leucokinin-immunoreactive neurons (SELKs) in the subesophageal ganglion are Dimm negative and display significant increase in cell size only after ectopic Dimm/dInR expression (using Lk-Gal4). (D) PDF-Gal4 is utilized for driving expression of Dimm and dInR in PDF-producing clock neurons (sLNv) of the brain. These neurons are located in ventral lateral part of the larval brain and have axon terminations dorsally. Both Dimm and Dimm/dInR expression give rise to larger cell bodies (cb) of sLNv neurons. (E–H) Quantification of cell body sizes after ectopic expression of Dimm, dInR or Dimm/dInR compared to controls (Gal4 crossed to w1118). Data are presented as means ± S.E.M, n = 6–36 flies for each genotype from three independent crosses (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 as assessed by unpaired Students' t-test). Scale bar = 20 μm in (A–D).