Figure 7.
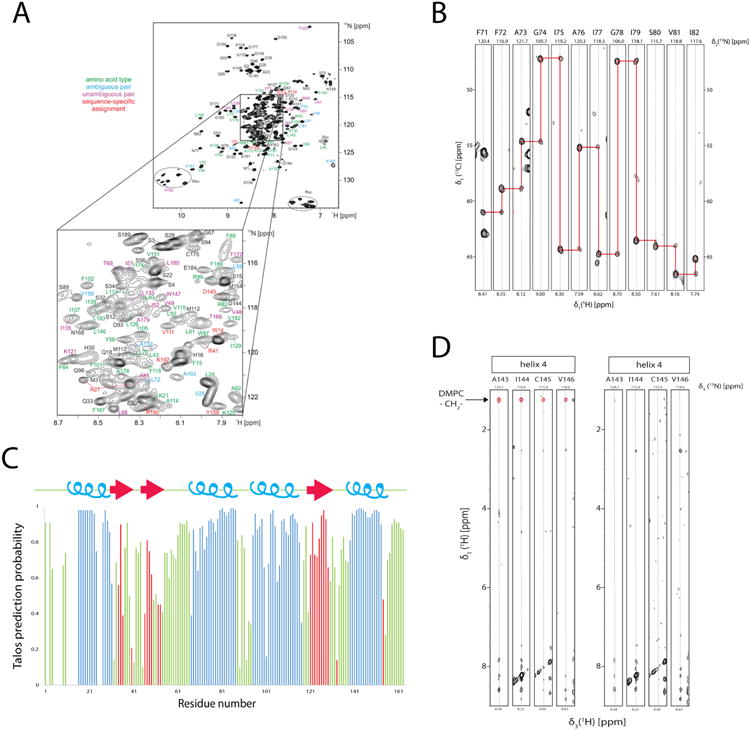
Backbone amide and 13Cα assignment and secondary structure determination of LspA in dH5 DMPC ND titrated with diC7PC. (A) Overview of assignment of backbone amide signal of LspA. For residues with colored annotations the following information was obtained from combinatorial 15N, 13Cα, and 13C' labeling: green, only the amino acid was determined, blue, ambiguous sequential pairs (two possibilities for the amino acid type preceding the detected amide), magenta, unambiguous pairs (both amino acid types of a i-1, i pair determined, and red, unique pairs (i.e. the i-1 / i amino-acid type combination occurs only once in the sequence. (B) Example strips taken from 3D HNCA experiments show the spectral quality although without the backbone assignment from the combinatorial labeling strategy would have been very difficult due to degeneracy in 13Cα chemical shifts and prior knowledge of preceding residues gained from the combinatorial labeling strategy. (C) Secondary structure prediction taken from the program Talos+ indicates 4 helices (blue) and 3 β-strands (red) in the loop regions. (D) Strips from two 3D 15N-resolved 1H,1H NOESY spectra for residues in TM4. Two samples of 2H/15N-labeled LspA in deuterated diC7PC:protonated DMPC (left) and protonated diC7PC :deuterated DMPC (right) titration, measured at 45° at 950 MHz are shown. Residues in helix 4 have NOEs to the DMPC fatty acid methylene chain at 1.25 ppm (red) only when in protonated DMPC samples. Protonated diC7PC methylene signals are not apparent in either sample.
