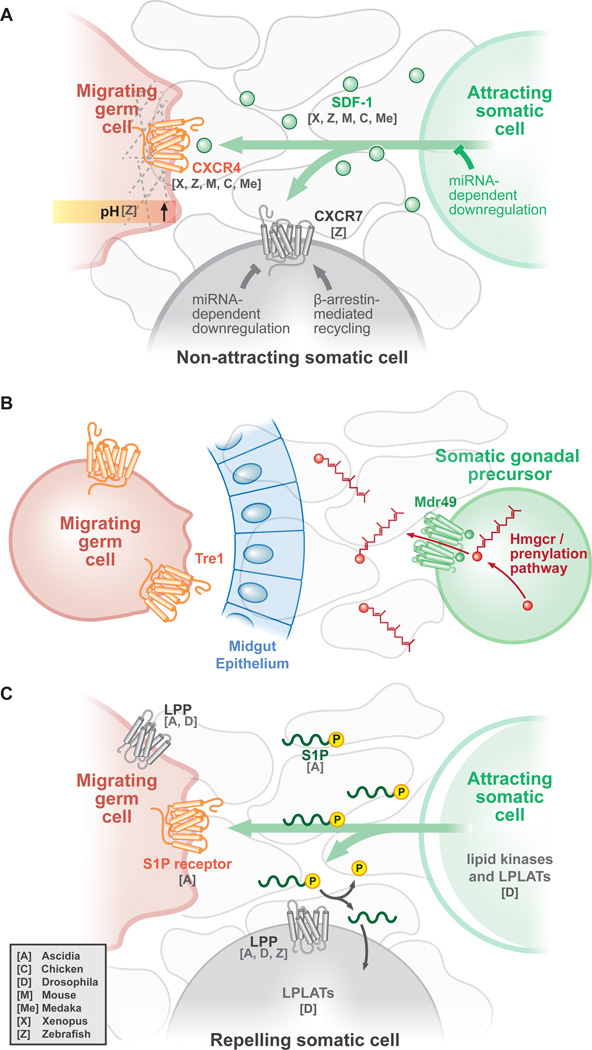
Figure 3. Germ cells are guided to the gonad by one or more environmental cues.
Shown here are three simplified schematics, each with three cell types: germ cell-attracting somatic cells (green), migratory germ cells (red) and non-attracting somatic cells (gray) A. The SDF-1/CXCR4 axis functions in many vertebrates. The attracting somatic cell secretes the chemoattractant SDF-1 (small green circles), which either binds to the CXCR4 GPCR in the migrating germ cell or is taken up by the molecular sink GPCR CXCR7 in non-attracting somatic cells. Factors recently identified as promoting or inhibiting ligand or receptor components are highlighted. B. Study of the invertebrate Drosophila model has revealed other guidance mechanisms, wherein HMGCR, additional factors required for protein prenylation, and the ABC transporter Mdr49 are required in somatic attracting cells for germ cell guidance by a secreted factor (red). Germ cells require the GPCR Tre1 for exit from the midgut and migration to the gonad. C. Extracellular lipids guide germ cell migration in highly divergent species. Phospholipids are produced by attracting somatic cells, which can bind to receptors such as the S1P receptor in migrating germ cells. To amplify the phospholipid gradient, nonattracting somatic cells express lipid phosphate phosphatases (LPP), which depletes the local environment of phospholipids. The model organism for which specific factors and processes have been discovered is noted as a single letter with the key code in the bottom left corner.