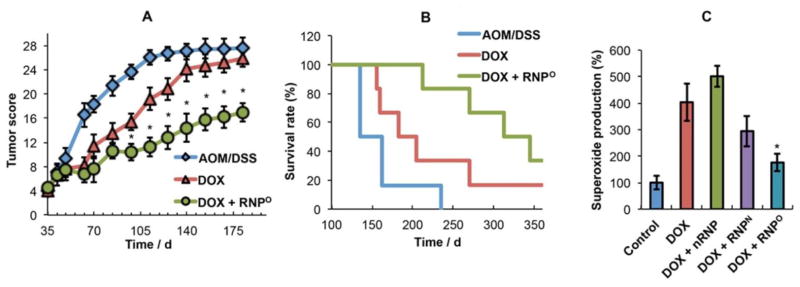
Figure 12.
Efficacy of oral redox nanoparticles (RNPo) in combination with intravenous doxorubicin (DOX) in azoxymethane-dextran sulfate sodium (AOM/DSS) induced colitis associated cancer in mice evaluated by (A) colonic tumor score, (B) survival, and (C) superoxide production in the heart. DOX (5 mg/kg) was injected i.p. in mice once a week, while RNPo (2.5 mg/mL) were administered to mice in free drinking water starting on day 35, and the treatments were stopped on day 70. DOX + RNPo combination treatment showed enhanced anti-cancer efficacy and less cardiotoxicity as compared to DOX (*p < 0.05). Adapted from [203] with permission.