Figure 1.
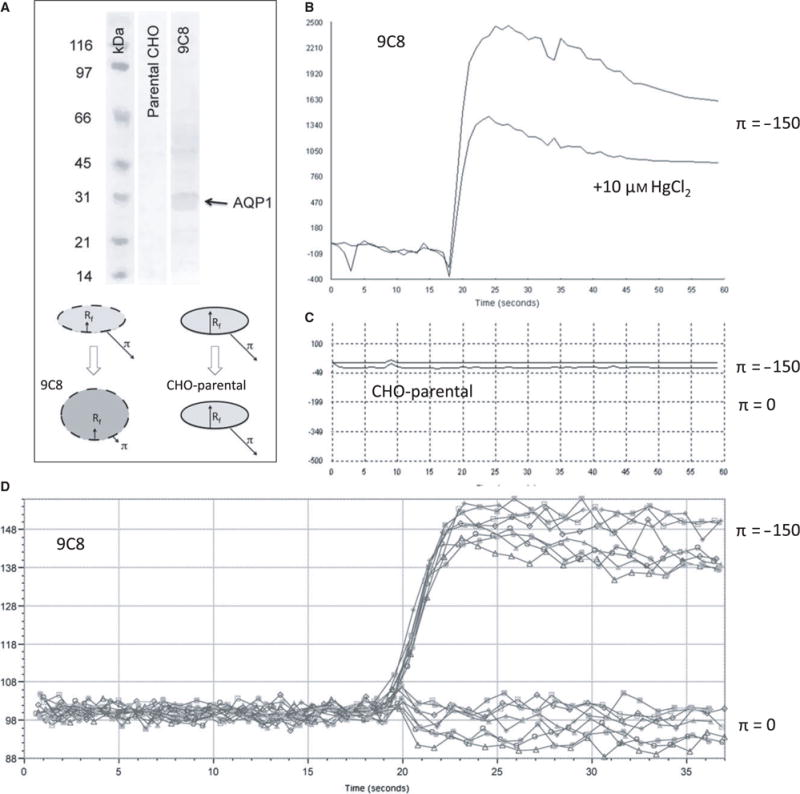
Simultaneous calcein dequenching of confluent AQP1-expressing CHO cells using a robotic plate reader: (A) Western blot of CHO-K1 cells and CHO-9C8 AQP1-expressing cells (top), using an anti-AQP1 antibody (a.a. 243–261) (Millipore, Temecula, CA, USA). The cartoon (bottom) indicates the swelling of AQP1 cells by osmotic shock, while cells without AQP1 channels do not swell notwithstanding the presence of the osmotic shock. (B) Characteristic fluorescence response showing a rapid rise in fluorescence as the result of dequenching of entrapped calcein. HgCl2 reduces the extent in signal with a small effect in the rise time. (C) CHO cells without AQP1 do not respond to an osmotic pressure. (D) Representative data from a 96-well experiment, showing responses of AQP1-expressing cells in the absence (bottom curves) and presence (top curves) of an osmotic gradient.
