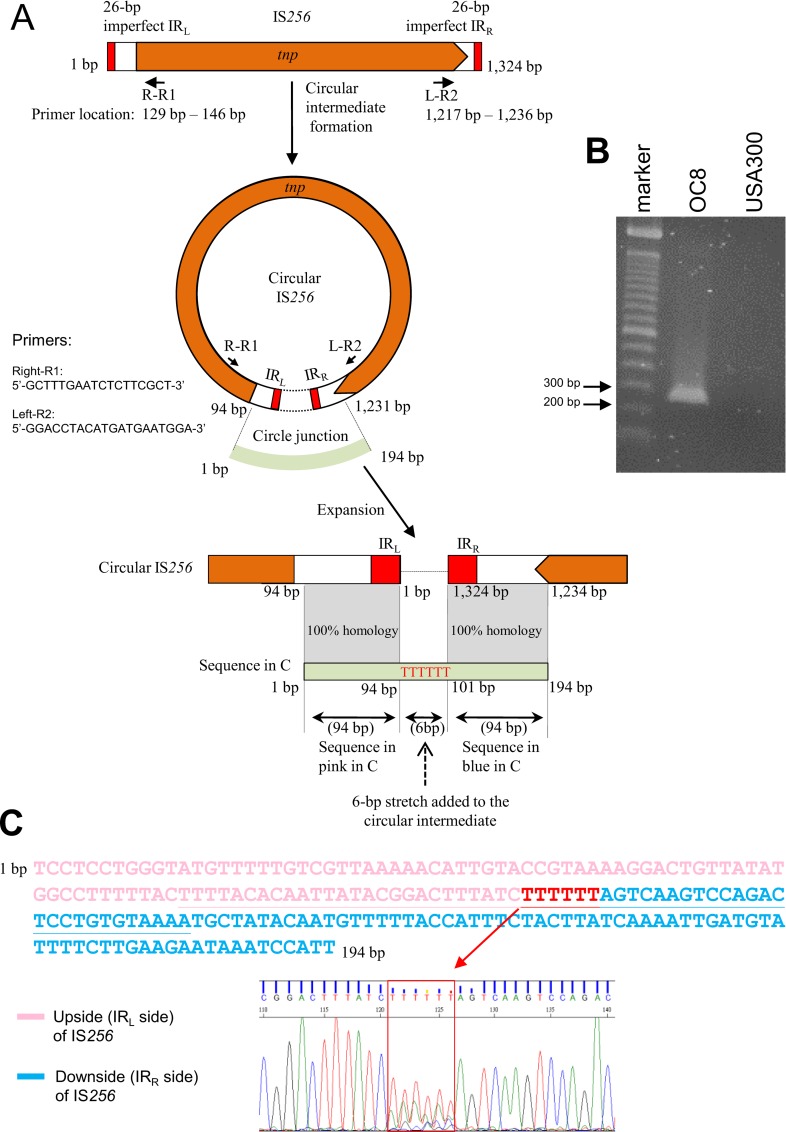
Fig 4. The structure of IS256 and its extrachromosomal circular DNA in OC8.
In A, the structure of IS256 (OC8) is based on the OC8 genome sequence (GenBank accession number AP017377); the structure was very similar to previously described IS256 structures [27,48,49]. PCR primers to detect an IS256 circular DNA were designed based on the OC8 genome sequence. In B, the PCR primer set (R-R1 and L-R2, shown in A) exactly detected IS256 circular DNA for OC8 (PCR product size, approximately 200 bp), while there were no amplified bands for strain USA300-0114, which lacked IS256. In C (and B), the 194-bp nucleotide sequence of the estimated PCR product, perfectly matched the IRL side and IRR side regions of IS256 (OC8), and contained a 6-bp stretch, marked in red; 26-bp imperfect IR sequences and 6-bp stretch sequences were underlined in C. However, the 6-bp stretch data showed a “mixed” result, with TTTTTT as the highest base content (followed by AAAAAA). Since the 6-bp stretch originates from a flanking att sequence [48] and OC8 carries 19 IS256 copies with distinct att sequences, the “mixed” 6-bp stretch reflects the presence of heterogeneous circular DNA (in terms of stretch sequences) in OC8. This observation is consistent with the AT-rich att sequences of 19 IS256 copies on the genome.