Fig. 4. ABL1 is a reader of the TIE2-modified H4Y51 histone mark.
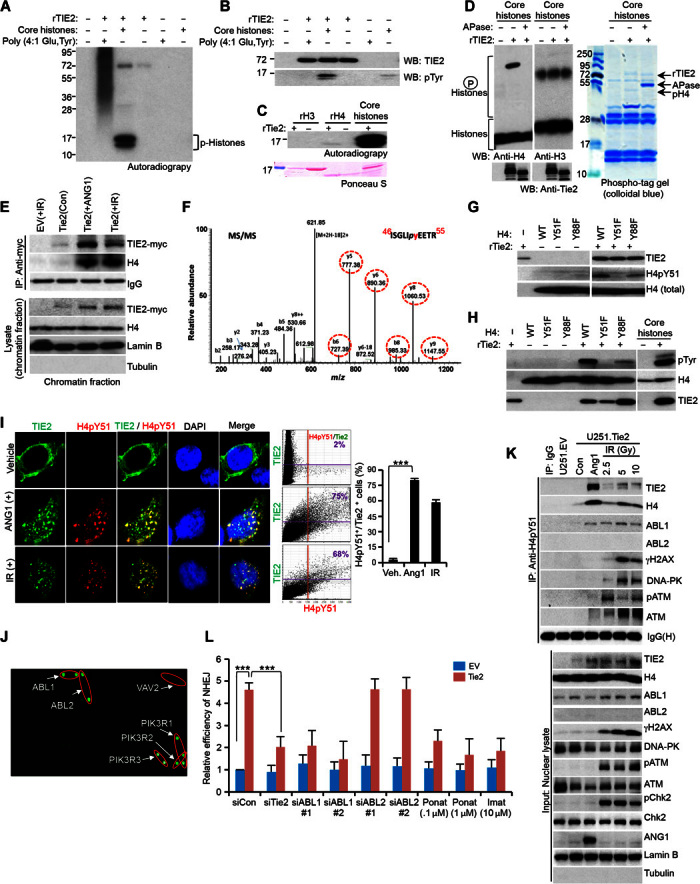
(A) rTIE2 potentially phosphorylates core histones. (B) rTIE2 potentially phosphorylates core histones at tyrosine residues. WB, Western blotting. (C) rTIE2 potentially phosphorylates rH4 but not rH3. (D) rTIE2 phosphorylates H4 as assayed using a phospho-tag gel. APase, alkaline phosphatase. (E) Cross-linked chromatin contains TIE2/H4 complexes upon ANG1 or IR stimulus. (F) Detection of phosphorylation of H4Tyr51 in the nucleosomes isolated from HEK293.Tie2 cells after ANG1 and IR exposure. Mass spectrometric analysis of a tryptic fragment at m/z mass/charge ratio of 630.7990 (mass error: 2.71 ppm) matched to the doubly charged phosphopeptide ISGLIpyEETR, suggesting that Y6 was phosphorylated. Mascot ion score was 52, with an expectation value of 6.5 × 10−5. Phosphotyrosine-containing peptide fragments are shown in dotted circles. MS/MS, tandem mass spectrometry. (G and H) Tyrosine phosphorylation of H4 analyzed using H4pY51 (G) and pTyr (H) antibodies with purified H4 mutant proteins. (I) Colocalization of TIE2 and H4pY51 in HEK293.Tie2 cells upon ANG1 and IR stimuli, as assessed by confocal microscopy. Colocalization was quantified with Olympus FluoView version 3.1a software. (J) rH4pY51 peptide binds to specific SH2 domain–containing proteins. (K) H4pY51 complexes with a panel of DNA repair proteins, including ABL1, in U251.Tie2-myc cells after IR exposure. (L) TIE2-induced NHEJ DNA repair is jeopardized by inhibiting ABL1 but not ABL2. Data represent means ± SD; **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.
