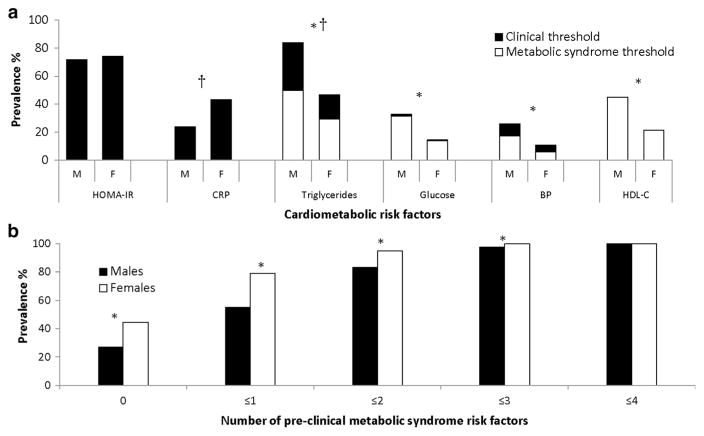
Figure 1.
(a, b) Prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factors in male and female adolescents. Clinical thresholds: HOMA-IR ≥ 3.16, CRP ≥ 3.0 mg/L, triglycerides ≥ 1.47 mmol/L, glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol/L and BP (currently taking medication for hypertension or SBP or DBP ≥ 95th percentile for sex, age and height for youth under 18, and ≥ 140/90 mmHg for 18 and 19 year olds). Pre-clinical or metabolic syndrome thresholds: triglycerides ≥ 1.24 mmol/L, glucose ≥ 5.55 mmol/L, BP (SBP or DBP ≥ 90th percentile for sex, age and height for youth under 18, and ≥ 130/85 mmHg for 18 and 19 year olds), HDL-C ≤ 1.04 mmol/L. Abbreviations: M, male; F, female; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; CRP, C-reactive protein; BP, blood pressure; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. †Significant sex difference in the prevalence of clinically elevated risk factors (p <0.05). *Significant sex difference in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome risk factors (p <0.05).