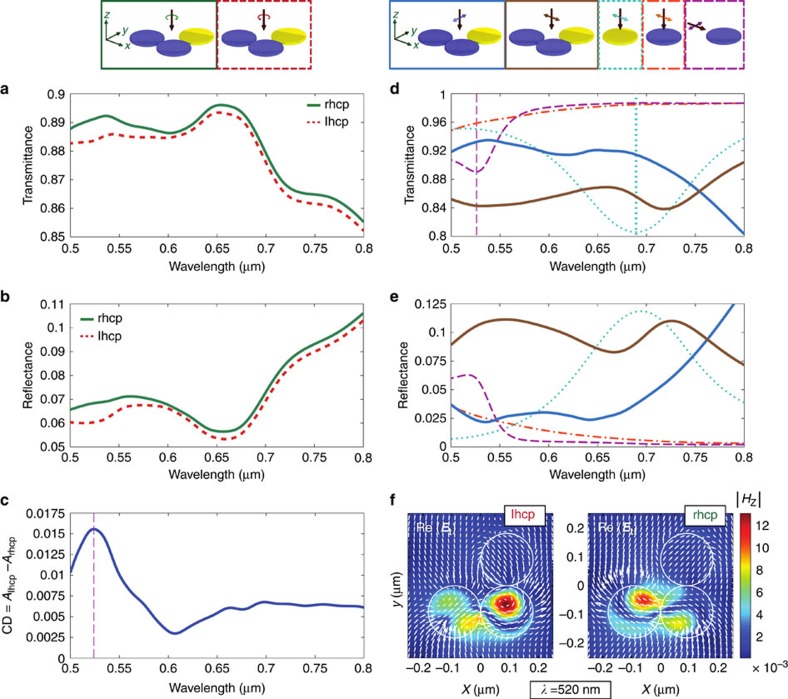
Figure 2. Numerical results for different nanodisks system.
Numerically calculated (a) transmittance and (b) reflectance spectra for an individual nanodisk trimer for left-handed circularly polarized (lhcp, dashed red line) and right-handed circularly polarized (rhcp; solid green line) light excitation. (c) Resulting circular dichroism (CD) curve. (d) Transmittance and (e) reflectance spectra for a trimer (solid blue and brown curves) and individual nanodisks (dotted and dashed curves) for linearly polarized excitation. The corresponding excitation schemes are indicated above (d). The vertical dotted cyan-coloured line indicates the spectral position of the electric dipole resonance of an individual Au nanodisk, whereas the vertical dashed magenta-coloured line marks the position of the magnetic dipole resonance of an individual Si nanodisk for the indicated excitation schemes. (f) Distributions of the instantaneous in-plane electric field (Et=(Ex, Ey); white arrows) and the modulus of the longitudinal magnetic field component (|Hz|; colour-coded) for a wavelength of 520 nm plotted in a plane parallel to the xy-plane cutting through the centers of the disks.