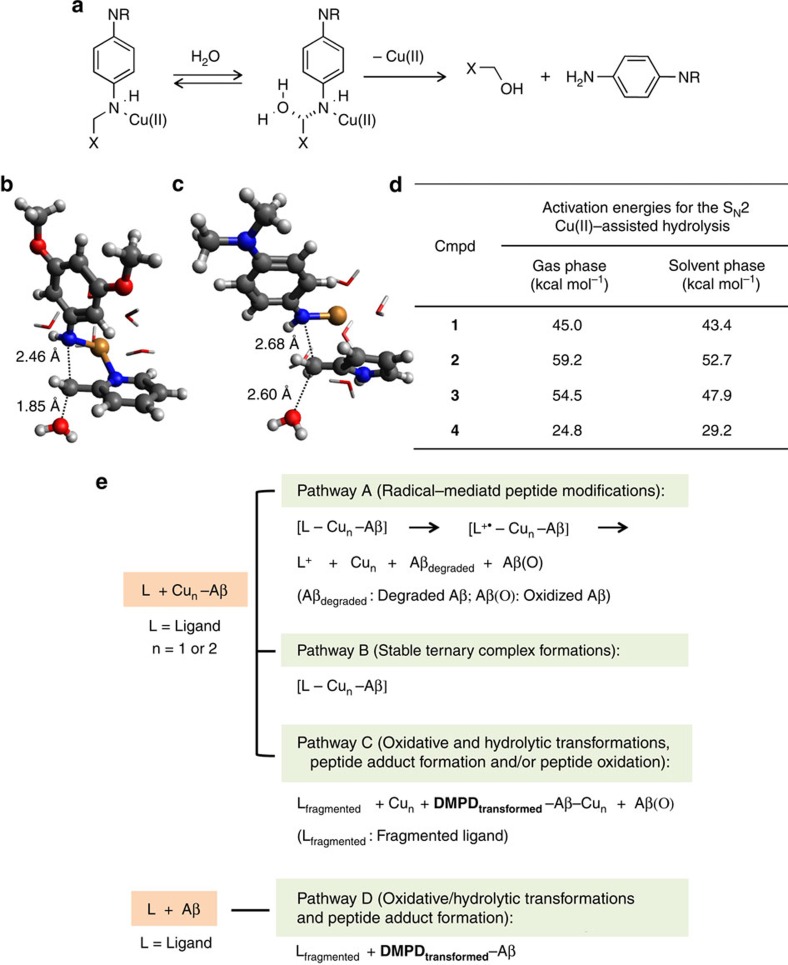
Figure 6. Computational investigations of the SN2 Cu(II)-assisted hydrolysis and proposed mechanisms.
(a) Scheme of the model used to calculate the SN2 Cu(II)-assisted hydrolysis of 1–4. (b,c) The calculated transition state structures of the hydrolysis of (b) 2 and (c) 4. The bond lengths of bonds being broken and being formed are shown. For clarity, the water molecules coordinated to Cu(II) are represented with sticks (red: O; blue: N; grey: C; white: H; orange: Cu). (d) Calculated activation energies for the SN2 Cu(II)-assisted hydrolysis in the gas and solvent (water) phases for 1–4. (e) Proposed mechanisms for the different activities of 1–4 towards metal-free or metal-associated Aβ species under aerobic conditions.