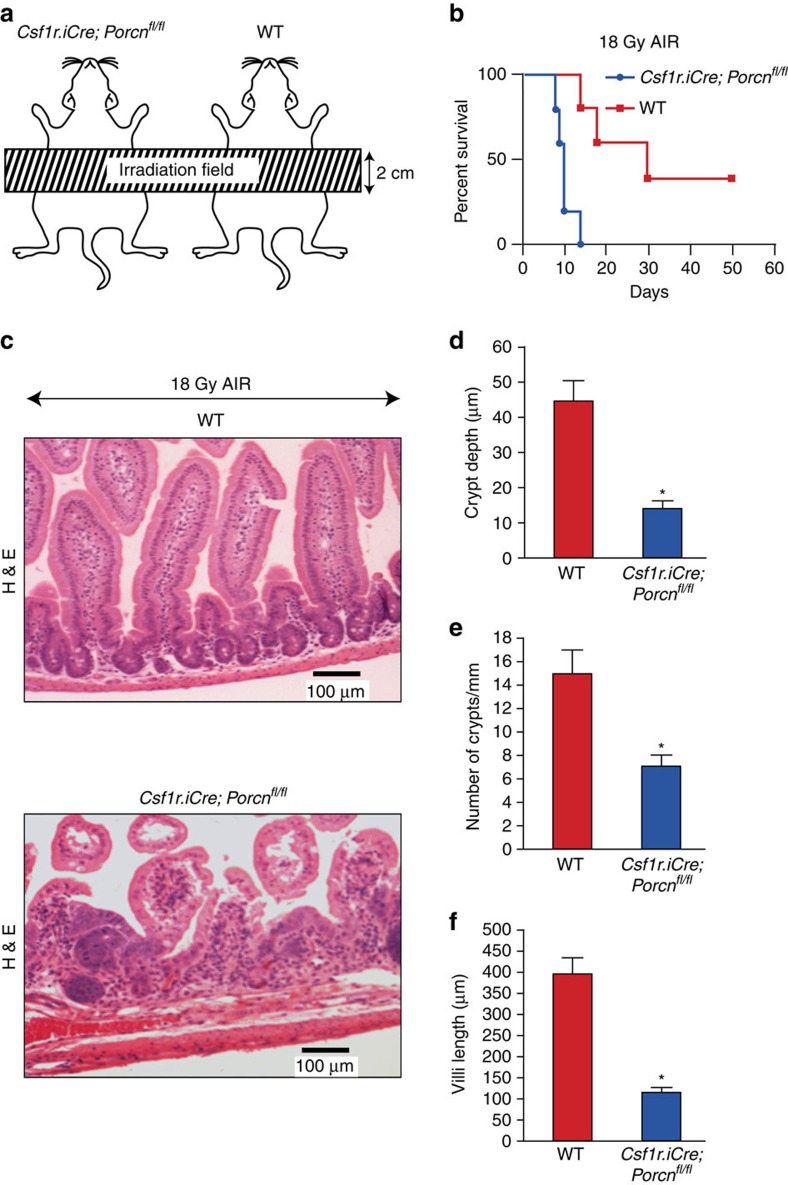
Figure 2. Deletion of Porcn in macrophages sensitizes mice against lethal dose of AIR.
(a) Schematic diagram demonstrating the AIR exposure field for Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl and WT mice. A 2 cm area of the mice containing the GI was irradiated (irradiation field), thus shielding the upper thorax, head and neck as well as lower and upper extremities, protecting a significant portion of the bone marrow, thus inducing predominantly RIGS. (b) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl mice have reduced survival against a lethal dose (18 Gy) of abdominal radiation compared with WT mice (n=10 per group; P<0.009 Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test). (c) HE staining of jejunum sections from Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl and WT mice exposed to 18 Gy AIR. Mice were killed and jejunum was collected at day 5 post irradiation. Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl mice showed more villi denudation and crypt loss compared with WT littermate mice at day 5 post irradiation (n=3 per group). (d) Histogram showing crypt depth (μM) in jejunal sections of Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl and WT mice exposed to 0 Gy or 18 Gy AIR. Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl mice exposed to AIR had significantly higher reduction in crypt depth compared with WT *P<9.64E−08 unpaired t-test, two-tailed. (e) Histogram showing number of crypts mm−1 in jejunal sections of Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl and WT mice exposed to 0 Gy or 18 Gy AIR. Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl mice exposed to AIR has significantly higher reduction in crypt number compared with WT *P<8.77E−09 unpaired t-test, two-tailed. (f) Histogram showing villus length in jejunal sections of Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl and WT mice exposed to 0 or 18 Gy AIR. Csf1r.iCre;Porcnfl/fl mice exposed to AIR has significantly higher reduction in villi length compared with WT *P<8E−07 unpaired t-test, two-tailed.