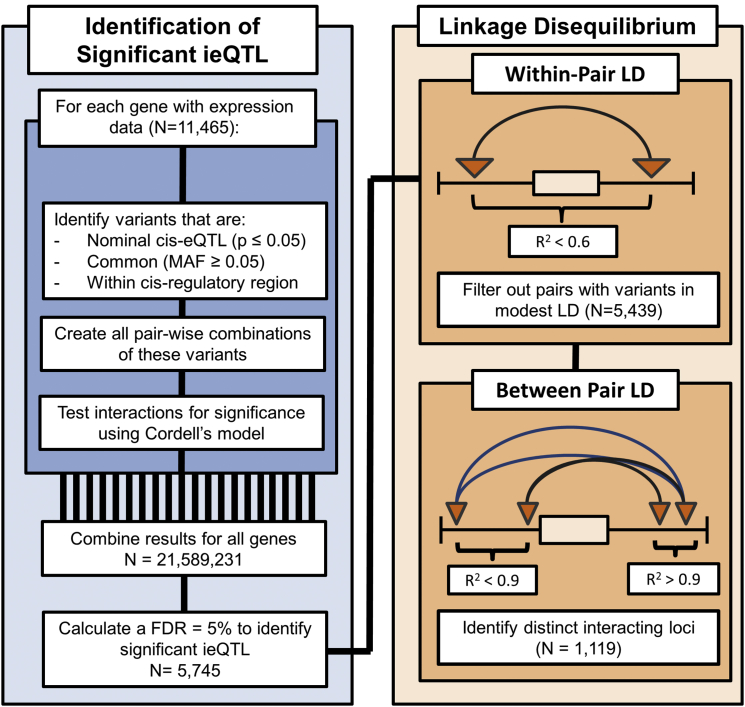
Figure 1.
Workflow Used to Identify and Group ieQTL
In the discovery analysis, nominally significant cis-eQTL (denoted by triangles) were paired together and tested for interactions significantly associated with gene expression levels (denoted by arcs). The within-pair LD was then calculated (Figure S1), and interactions composed of variants in modest LD (r2 > 0.6) with one another were removed from the remainder of the analysis. Some of the remaining interactions represented the same pair of interacting genomic loci (Figure S2) and were partitioned into distinct groups (denoted by the arc color). For two interactions to be grouped together, each SNP within one significant ieQTL model had to be in high LD (r2 ≥ 0.9) with a SNP within the second ieQTL model, and vice versa.