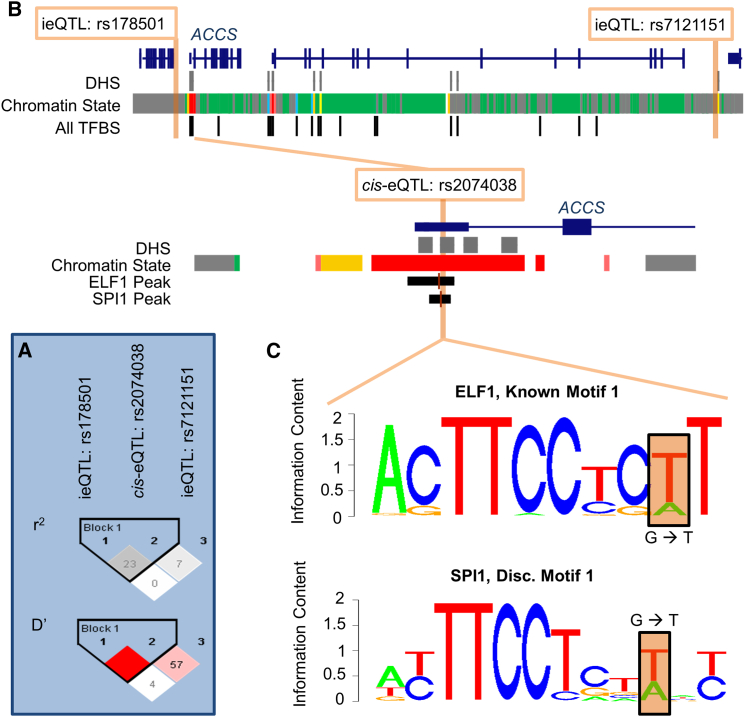
Figure 4.
The Interacting SNPs Regulating ACCS Are Probably Tagging a Single-Variant cis-eQTL through Linkage Disequilibrium
The interaction between rs178501 and rs7121151 is mediated by the cis-eQTL rs2074038 in the conditional analysis (interaction p value > 0.05).
(A) While the interacting variants are in low LD with the cis-eQTL based on r2, their high D′ indicates they often occur on the same haplotype.
(B) The interacting variants are not located within DNase hypersensitivity sites, predicted chromatin states with a regulatory function (GM12878 Combined), or any of the uniform binding peaks identified for all transcription factors tested in GM12878 by ENCODE; however, the cis-eQTL is located within the canonical promoter for ACCS, a DNase hypersensitivity site, and numerous transcription factor binding peaks identified in GM12878 by ENCODE.
(C) Notably, the cis-eQTL occurs within a binding peak for both ELF1 and SPI1 in GM12878 and also alters the binding motifs of these transcription factors at the position highlighted in orange. Thus, the cis-eQTL rs2074038 is probably the causal variant, and the interaction is simply capturing its effect through LD.