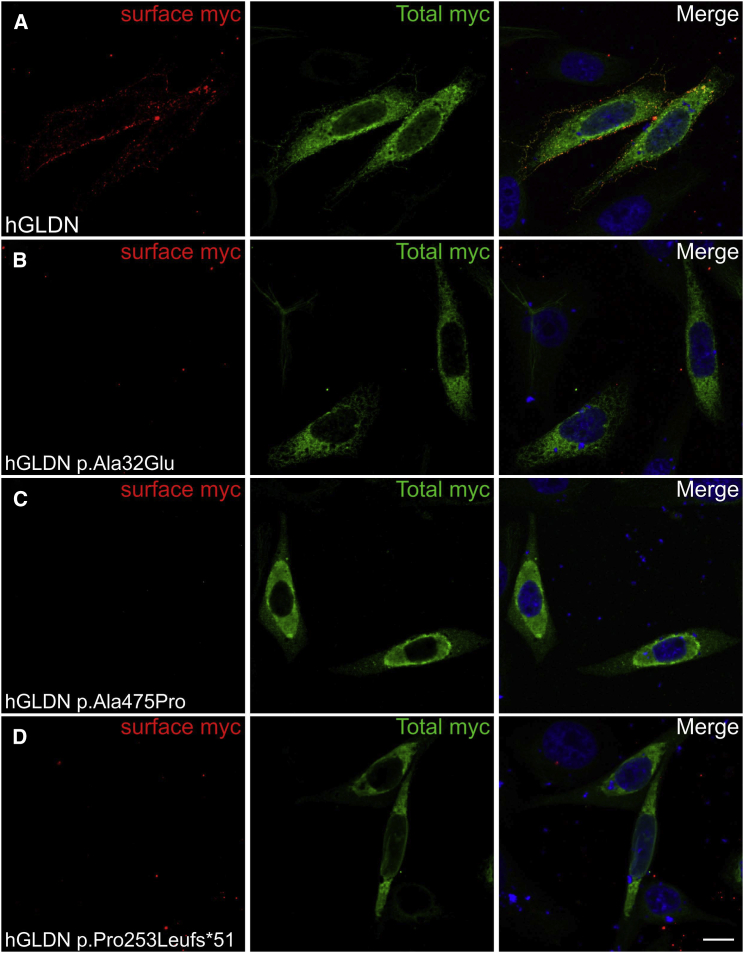
Figure 3.
Mutations in GLDN Affect the Surface Localization of the Protein
Human gliomedin cDNA was amplified by PCR from a human placental cDNA library and sub-cloned into pcDNA3.1 (Thermofisher) at KpnI and XbaI sites, and a myc-tag epitope was inserted at the extracellular C terminus. Mutations found in the affected individuals (c.1423G>C, c.758delC, and c.95C>A) were inserted into cDNA with PrimeSTAR HS DNA polymerase (Clontech). All constructs were sequenced through the entire coding region. CHO cells transfected with myc-tagged human gliomedin (hGLDN) were incubated with mouse antibodies against myc before fixation to label surface myc (red) and after fixation and permeabilization to label total myc (green). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). WT gliomedin (A) is readily localized at the cell surface. By contrast, p.Ala32Glu (B), p.Ala475Pro (C), and p.Pro253Leufs∗51 (D) variants strongly impacted the surface localization of gliomedin. Scale bars represent 10 μm.