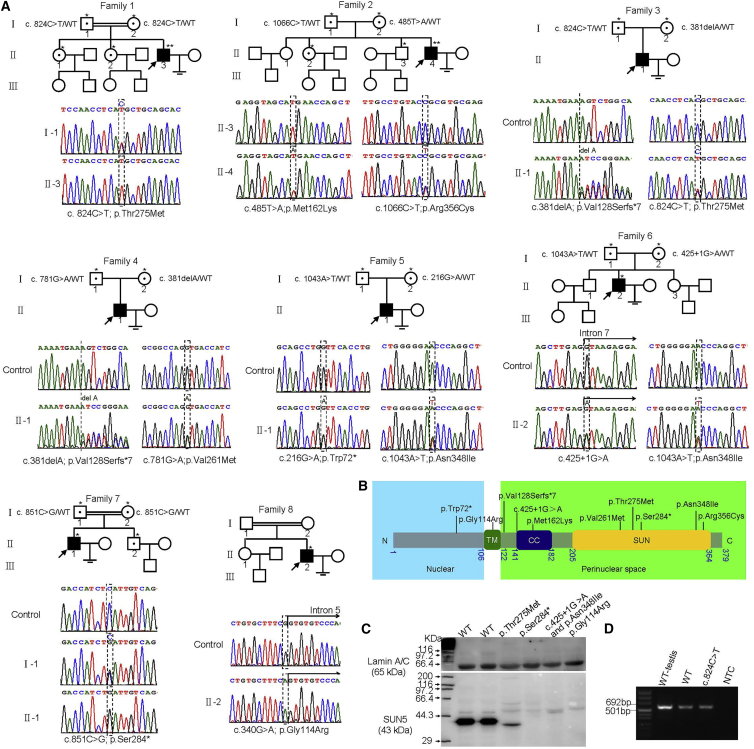
Figure 2.
Pedigrees and SUN5 Mutations in Families Affected by Acephalic Spermatozoa Syndrome
(A) Pedigrees of the eight families with inherited SUN5 mutations are shown. The individuals with a single star were Sanger sequenced. Individuals F1:II-3 and F2:II-4 were tested by WES (two stars).
(B) The domain architecture of SUN5 and the location of the SUN5 variants. The protein has 379 amino acids (gray) and contains a single transmembrane (TM) domain (green), a coiled-coil (CC) domain (blue), and a SUN domain (yellow). SUN5 is located on the inner nuclear membrane; the N terminus is in the nuclear space (light-blue background), and the C terminus extends to the perinuclear space (light-green background).
(C) Western blot showing Lamin A/C (Proteintech antibodies, 10298-1-AP) and SUN5 (Proteintech antibodies, 17495-1-AP) levels on ejaculated sperm from two control individuals and four affected individuals with SUN5 variants. Molecular weights, showed in the left lane, were determined according to the protein molecular weight marker (Takara, broad range, 3452Q).
(D) Agarose gel image of cDNA PCR products encompassing exons 10–13 of SUN5 (forward primer 5′-CCTGAAGTCTATAGGGGCCA-3′; reverse primer 5′-ATCTCTCTTAGGGTAGGGGTTC-3′). A single band of expected size was detected in individual F1:II-3, with the c.824C>T (p.Thr275Met) mutation, suggesting that this variant does not affect splicing. WT testis is a sample from an individual with prostate cancer who underwent bilateral castration treatment. NTC represents negative control.