Figure 1.
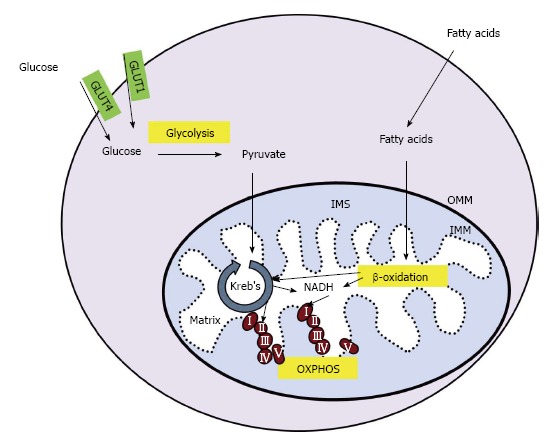
Cellular energy production. In skeletal muscle, glucose enters the cell through glucose transporter type 1 or 4 (GLUT1 or GLUT4, respectively). Glucose is converted to pyruvate in the glycolysis pathway. Pyruvate is transported across the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes (OMM and IMM, respectively) and into the mitochondrial matrix where it is converted into acetyl-coA. Fatty acids undergo β-oxidation in the mitochondria, creating acetyl-coA and NADH. Acetyl-coA is utilized by the Kreb’s cycle, creating NADH and succinate which enter the electron transport chain (ETC) at complex I and II, respectively. The movement of electrons through the ETC is coupled to the production of ATP in a process called OXPHOS. IMS: Intermembrane space; OXPHOS: Oxidative phosphorylation.
