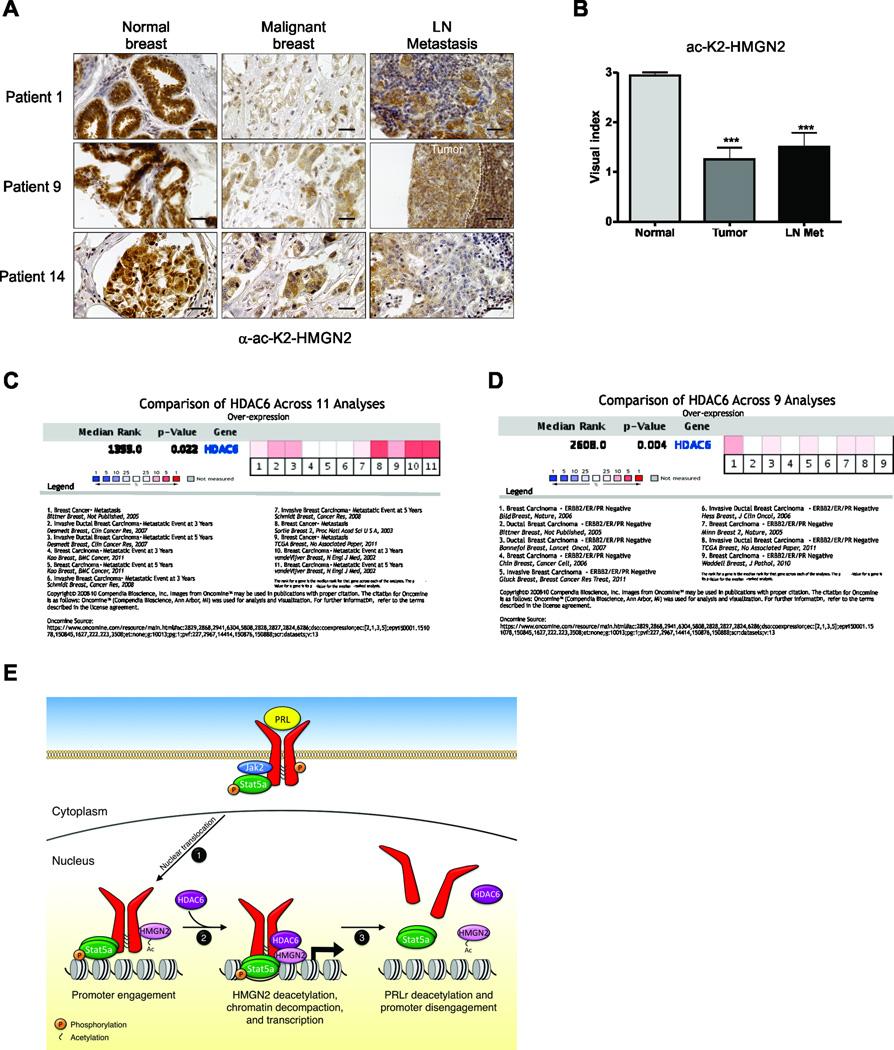
Figure 7. HMGN2 acetylation on residue K2 is lost during malignant progression of human breast cancer.
(A) A breast cancer progression array consisting of 14 patient-matched samples of normal human breast, primary tumors, and lymph node metastases were subjected to IHC analysis of ac-K2-HMGN2. Representative images of α-ac-K2-HMGN2 IHC of 3 separate patients is shown. Scale bar = 40µm. (B) Quantification of the entire breast cancer progression array shown in (A). (C) Meta-analysis of HDAC6 expression in 11 breast cancer datasets for patients who have a metastatic event within 3 or 5 years. (D) Meta-analysis of HDAC6 expression in 9 breast cancer datasets for triple negative disease. (E) Schematic of Stat5-mediated signaling: 1) Ligand binding induces phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of the Stat5a complex to PRL-induced target genes; 2) HDAC6 deacetylates PRLr-bound HMGN2 and allows chromatin decompaction and efficient Stat5a-mediated transcription of target genes; 3) Acetylation of HMGN2 and dissociation of the PRLr/Stat5a/HMGN2 complex from DNA. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroini multiple comparisons test was used for statistical analysis, *** p<0.001.