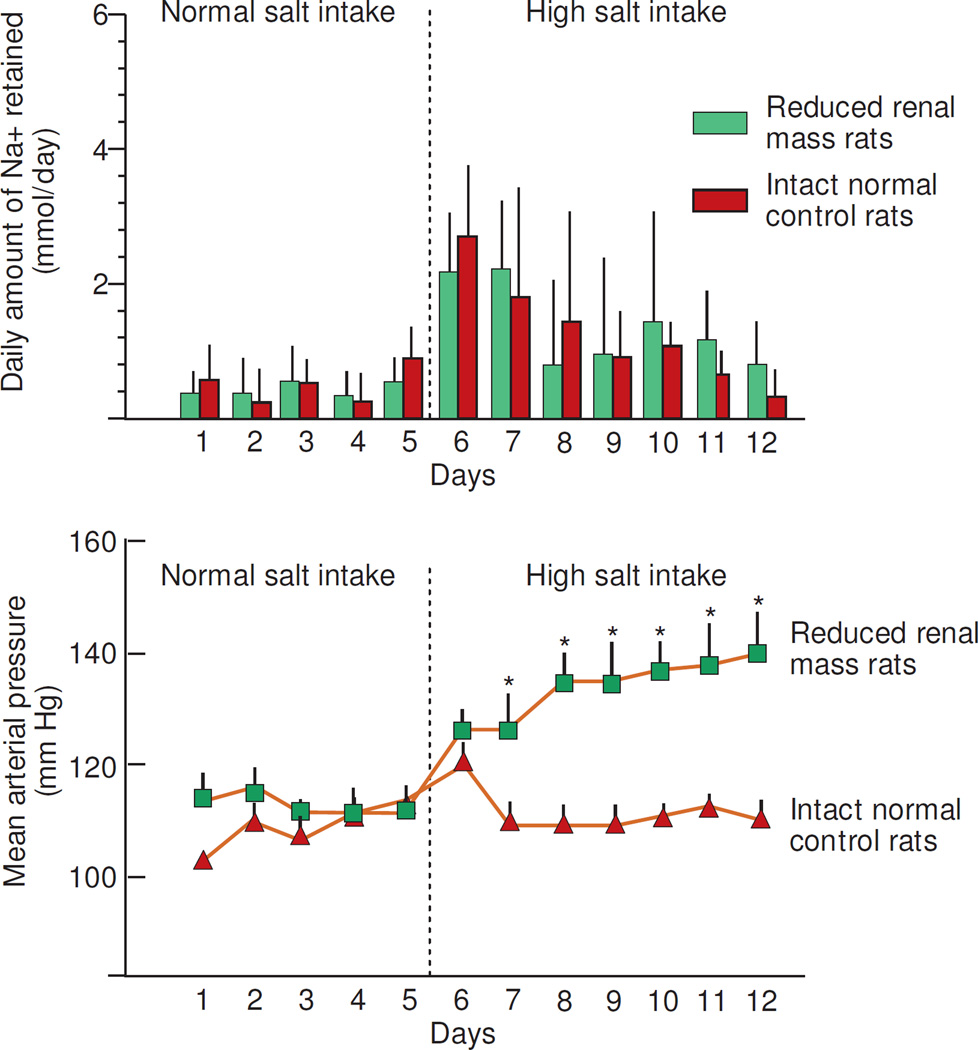
Figure 5.
Results of studies in which Kanagy and Fink measured daily sodium balance and mean arterial pressure before and after increasing salt intake in Sprague Dawley normal control rats with intact kidneys (n=8) and in Sprague Dawley rats with surgically reduced renal mass (reduced by 80%) (n=7) (adapted from Kanagy and Fink).32 Normal salt intake was provided by a "sodium-deficient" chow plus IV administration of 2 mmol NaCl per day in 5 mL of water and the high salt intake was provided by the "sodium-deficient" chow plus IV administration of 6 mmol NaCl per day in 5 mL of water. * denotes P <.05 group differences in blood pressure.