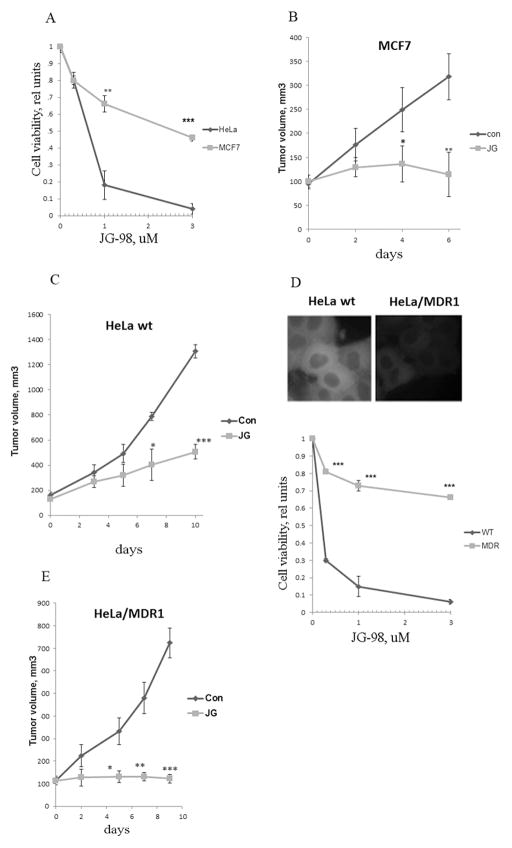
Fig. 1. Tumor stroma contributes to the anti-cancer effect of JG-98.
A. Sensitivity of cancer cell lines to JG-98 cell in culture. MCF7 and HeLa cells were treated with indicated concentrations of JG-98, and their viability was measured. Data shown are means+/− SEM of triplicates, here and below *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Student t-test. B. C. Sensitivity of MCF7 (B) and HeLa cells (C) to JG-98 in vivo. Xenograft tumors were established in nude mice. When tumors reached 100mm3 JG-98 was administered. Data shown are means +/− SEM for 10 tumors per group (B) or 6 tumors per group (C). D. Expression of MDR1 leads to resistance of cells to JG-98. Upper panel: Intracellular fluorescence of JG-98 in HeLa cells and HeLa/MDR1 cells. Lower panel: Sensitivity to JG-98 of HeLa and HeLa/MDR1. Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of JG-98, and cell viability was measured. Data shown are means+/− SEM of triplicates. E. Sensitivity of HeLa and HeLa/MDR1 cells to JG-98 in vivo. When xenograft tumors reached 100mm3, JG-98 was administered. Data shown are means +/− SEM for 5 tumors per group.