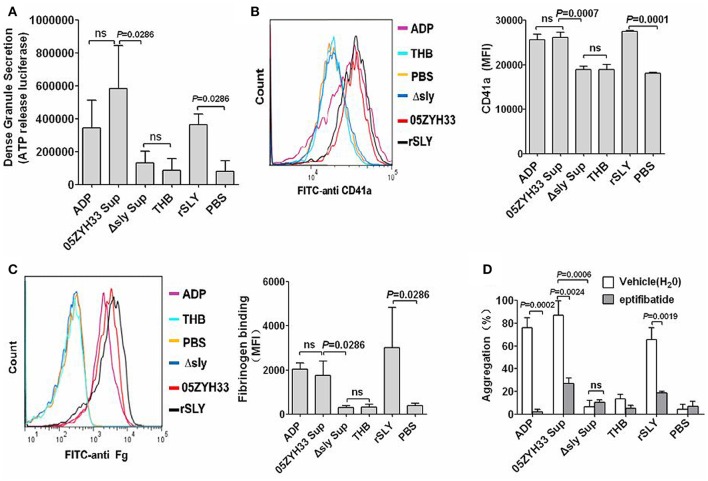
Figure 2.
Platelet activation by SLY, and GPIIb/IIIa (CD41a) mediated the SLY-induced platelet aggregation. (A) SLY induces dense granule release from platelets. PRP was incubated with S. suis culture supernatant or SLY protein (1 μg/ml). The Mann–Whitney U-test was used for statistical analysis. (B,C) S. suis culture supernatant or rSLY protein (1 μg/ml)-induced surface GPIIb/IIIa (CD41a) increase and fibrinogen binding to platelets in human blood was assessed by flow cytometry (Methods Section). Representative histograms for the MFI of CD41a/fibrinogen binding are shown in (B, left panel). Unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test was used for (B) statistical analysis. Mann–Whitney U-test was used for (C) statistical analysis. (D) PRP was preincubated with eptifibatide (10 μM) for 15 min prior to addition of S. suis supernatant or SLY protein. Platelet aggregation was expressed as a final percentage of light transmission. Unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test was used for statistical analysis. ADP (20 μM) was used as the positive control for platelet activation. THB and PBS were the negative controls for the culture supernatant and proteins, respectively. Data in panels (A–D) are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, with each experiment using blood from a different donor. P < 0.05 is considered to be the threshold for statistical significance; ns, not significant; 05ZYH33, wild type strain; Δsly, isogenic mutant of sly; Sup, supernatant; rSLY, recombinant SLY.