Figure 2.
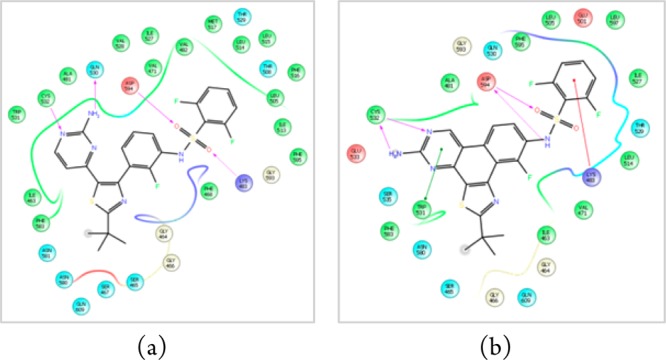
Modeled ligand interaction diagrams of (a) dabrafenib (1) and (b) dabrafenib_photo (2) in the active site of BRAFV600E (pdb 4XV2). Key ligand–protein interactions are shown. H-bonds between the ligand and the protein backbone are indicated by purple arrows. The binding modes of both compounds are closely related: The aminopyrimidine moieties of both compounds address the hinge region of the kinase by two H-bonds. The sulfonamide residues, respectively, bind to the aspartate594 via one (1) or two (2) H-bonds. The difluorobenzene moieties occupy the deeper hydrophobic pocket I, and the tert-butyl residues are exposed to the solvent.
