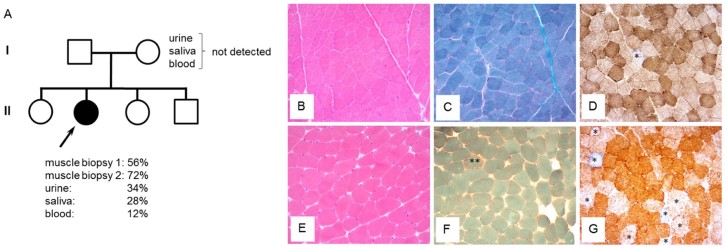
Fig. 2.
mtDNA mutation analysis in the patient and her mother (A) Family tree identifying the proband (highlighted by an arrow) with the m.5540G>A mutation. Analysis of several samples from the patient's clinically-unaffected mother strongly suggested that the m.5540G>A mutation has arisen de novo. (B–D) A first muscle biopsy, performed at the age of 28 years, shows normal muscle architecture in the H&E (B) and modified Gomori trichrome (C) stains and only occasional COX-deficient fibres (asterisked) identified following sequential COX/SDH histochemistry (D). (E–G) A second muscle biopsy, performed 13 years later, shows slightly rounded muscle fibres (E), an occasional ragged-red fibre (**) and an apparent increase in the number of COX-deficient fibres and those with diminished COX reactivity (asterisked, G).