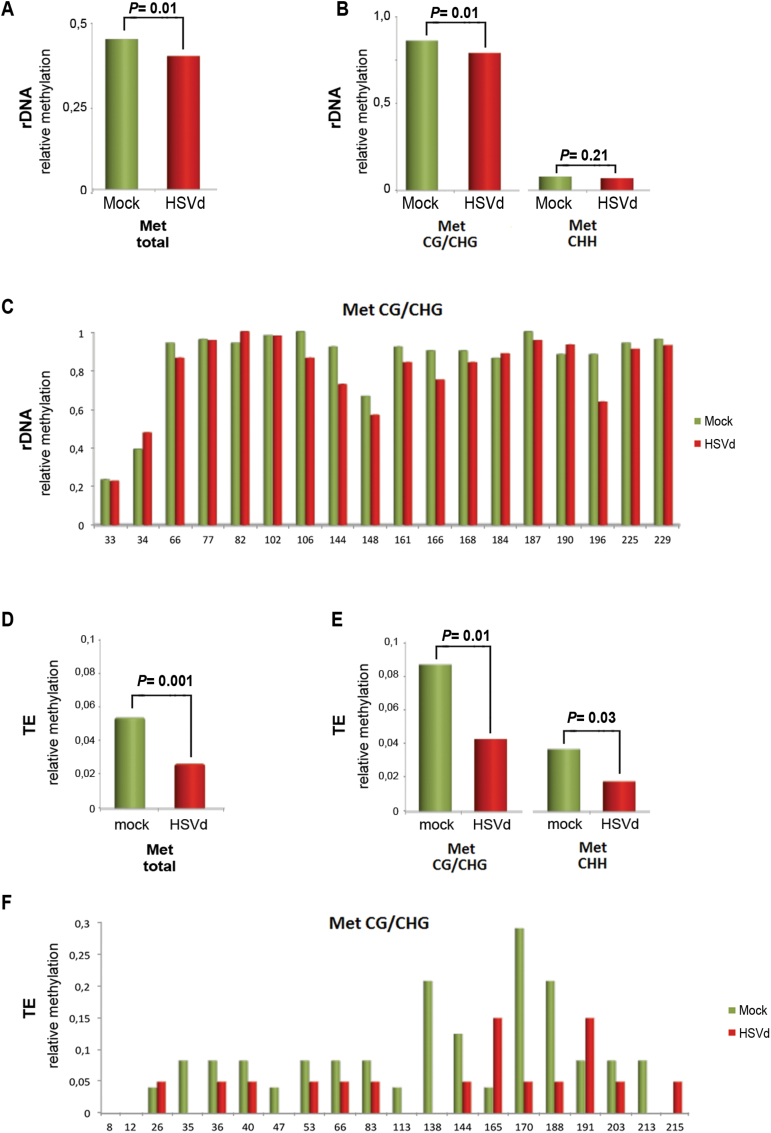
Fig. 4.
HSVd infection affects the methylation patterns of rRNA genes and TE in pollen grains. (A) The relative (HSVd/Mock) total rDNA methylation levels. Total methylation means are 0.40 (mock) and 0.37 (HSVd). Statistical differences were determined using a paired t-test. (B) Analysis of symmetric and asymmetric cytosine methylation levels in analysed samples of rDNA. Symmetric methylation means are 0.89 (mock) and 0.83 (HSVd). Asymmetric methylation means are 0.06 (mock) and 0.05 (HSVd). Statistical differences were determined using a paired t-test. (C) Position-specific relative methylation levels in CG and CHG contexts in the analysed samples of rDNA. (D) Relative (HSVd/Mock) total TE methylation. Total methylation means are 0.055 (mock) and 0.022 (HSVd). Statistical differences were determined using a paired t-test. (E) Analysis of symmetric and asymmetric cytosine methylation in the analysed samples of TEs. Symmetric methylation means are 0.084 (mock) and 0.041 (HSVd). Asymmetric methylation means are 0.037 (mock) and 0.018 (HSVd). Statistical differences were determined using a paired t-test. (F) Position-specific relative methylation levels in CG and CHG contexts in the analysed TEs. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)