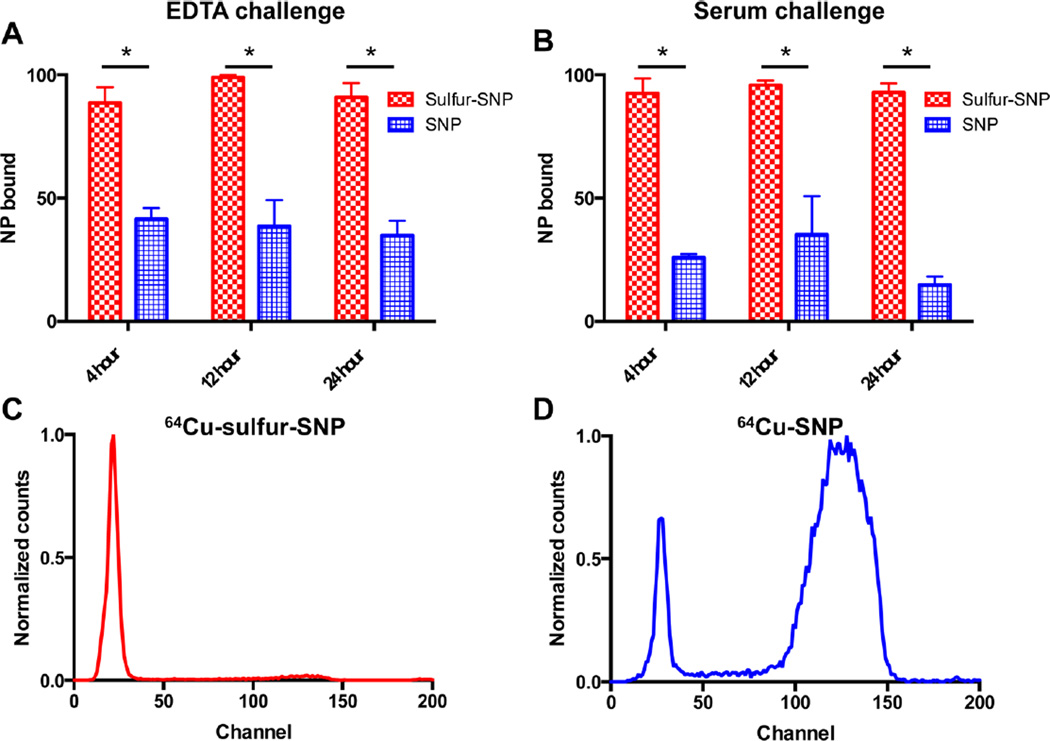
Figure 3.
Sulfur-SNP show significantly increased binding of 64Cu compared to native SNP. 64Cu shows significantly more stable binding to sulfur-SNP compared to SNP in an (A) EDTA challenge over 24 h, and (B) in a serum stability study, a prerequisite for in vivo use. (Data presented as mean with standard deviations; p < 0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test). Instant thin-layer-chromatography at 24 h shows (C) 64Cu binds stably to sulfur-SNP, whereas (D) 64Cu dissociates from native SNP when challenged in serum, respectively.