Table 1.
Optimization of reaction conditions.a
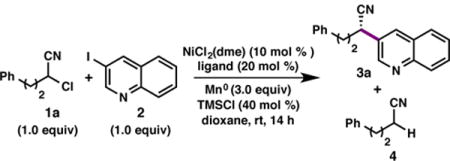
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entrya | Ligand | Deviation from Standard Conditions | Yield 3 (%)b |
Yield 4 (%)b |
ee 3 (%)c |
| 1 | L6 | None | 78 | 20 | 84 |
| 2 | L1 | DMA instead of dioxane | 0 | 62 | – |
| 3 | L1 | – | <5 | 32 | 38 |
| 4 | L2 | – | 17 | 22 | 9 |
| 5 | L3 | – | 25 | 40 | 83 |
| 6 | L4 | – | 0 | 32 | – |
| 7 | L5 | – | 52 | 35 | 77 |
| 8 | L6 | No Ni | 0 | 0 | – |
| 9 | L6 | No Mn0 | 0 | 0 | – |
| 10 | L6 | No TMSCl | <5 | <5 | 82 |
| 11 | – | No Ligand | 4 | 23 | 0 |
| 12 | L6 | Zn0 instead of Mn0 | 25 | 32 | 10 |
| 13 | L6 | TFA (0.4 equiv) | 48 | 37 | 78 |
| 14 | L6 | NaBF4 (1.0 equiv) | 76 | 24 | 90 |
| 15 | L6 | NaI (0.25 equiv) | 71 | 29 | 84 |
| 16 | L6 | RBrCN (5) instead of 1 | 9 | 36 | 84 |
Reactions conducted under inert atmosphere on 0.1 mmol scale for 14 h.
Determined by 1H NMR versus an internal standard.
Determined by SFC using chiral stationary phase.
