Figure 3.
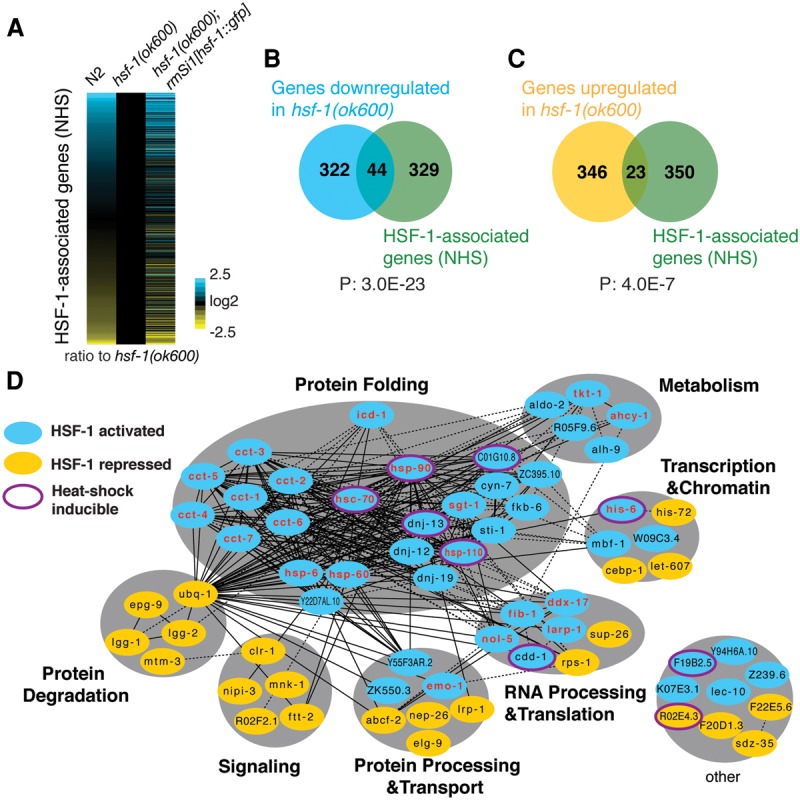
HSF-1 directly regulates genes essential for C. elegans larval development. (A) Relative expression of HSF-1-associated genes in wild-type (N2), hsf-1(ok600), and hsf-1(ok600); rmSi1[hsf-1::gfp] L2 animals (30 h after egg lay) at 20°C. Gene expression levels were determined by RNA-seq and normalized to that in hsf-1(ok600). (B,C) Venn diagrams showing the overlap of genes down-regulated (B) or up-regulated (C) in hsf-1(ok600) compared with N2 (FDR 0.05) and genes associated with HSF-1. P = Fisher's exact test. (D) The gene network directly regulated by HSF-1 in C. elegans larval development. HSF-1 directly activated genes corresponding to those genes directly associated with HSF-1 and down-regulated in hsf-1(ok600) (indicated in blue ovals); HSF-1 directly repressed genes corresponding to genes associated with HSF-1 and up-regulated in hsf-1(ok600) (indicated in yellow ovals). Solid lines represent physical protein interactions; dashed lines represent genetic interactions or coexpression. The 22 genes labeled in red are known to be required for larval development in genetic analyses. The eight genes induced upon heat shock are indicated with a purple outline around either blue or yellow ovals.
