Figure 1.
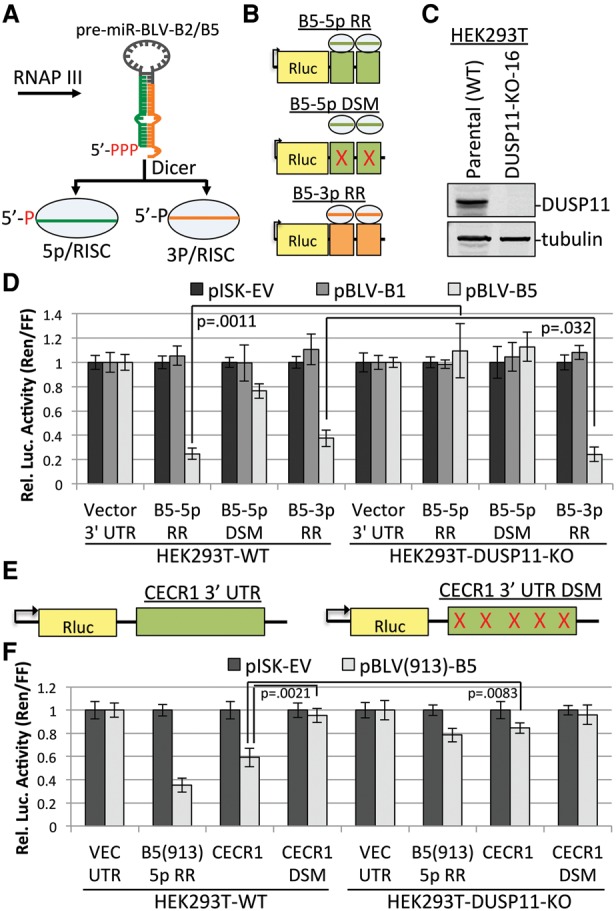
Knockout of DUSP11 decreases the RISC activity of the BLV 5p miRNAs. (A) Schematic diagram of the BLV miRNA biogenesis pathway. (B) Diagram of the BLV-B5 miRNA RISC reporters. Two sites complementary to either the 5p miRNA (green boxes) or the 3p miRNA (orange boxes) were inserted into the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of Renilla luciferase. In the B5-5p docking site mutant (DSM), point mutations were made in the sequence complementary to the B5-5p seed to interfere with RISC-mediated silencing. (C) Immunoblot analysis to confirm CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of DUSP11 in DUSP11 knockout clone 16 (DUSP11-KO-16) HEK293T cells as compared with the parental (wild-type [WT]) HEK293T cells. (D) Luciferase assay to measure the RISC activity of BLV-B5 miRNAs in parental (wild-type) and DUSP11 knockout clone 16 HEK293T cells. Bars represent the mean luciferase ratio (Renilla/firefly) ± SEM normalized to pISK-EV and the vector 3′ UTR reporter. Transfections were performed in triplicate in each experiment. Eight experiments were performed for vector 3′ UTR, B5-5p RR, and B5-3p RR cotransfected with pISK-EV and pBLV-B5. Four experiments were performed for vector 3′ UTR, B5-5p RR, and B5-3p RR cotransfected with pBLV-B1. Three experiments were performed for the B5-5p DSM with all expression vectors. (E) Diagram of the Rluc reporter containing the majority of the ovine CECR1 3′ UTR (green box), which has five potential target sites of BLV(913)-miR-B5-5p. Point mutations in all potential B5-5p target sites were made (red ×) to generate the Rluc CECR1 3′ UTR control vector (CECR1 DSM). (F) Luciferase assay measuring the repression of the CECR1 3′ UTR and B5-5p DSM by BLV-B5-5p in wild-type and DUSP11 knockout HEK293T cells. Bars represent the mean luciferase ratio (Renilla/firefly) ± SEM from four experiments. Values were normalized to pISK-EV and the vector 3′ UTR reporter.
