Figure 7.
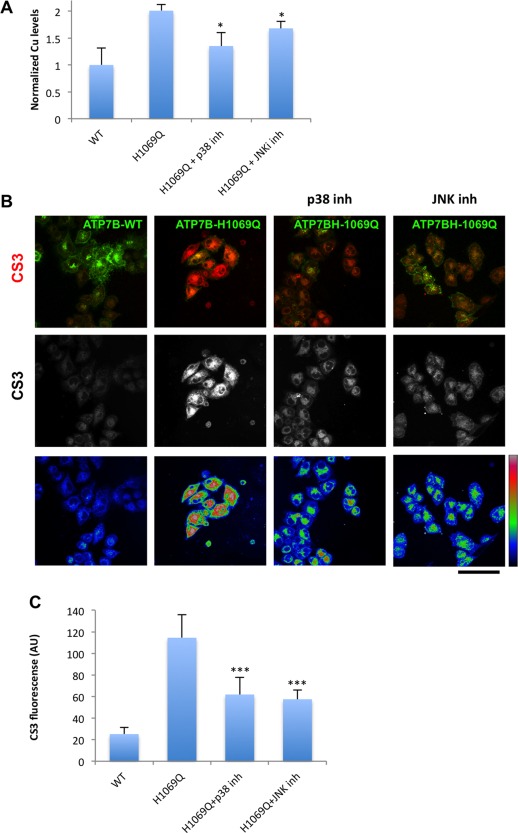
Inhibitors of p38 and JNK reduce Cu levels in cells expressing ATP7BH1069Q mutant. (A) HepG2 cells were infected with Ad‐ATP7BWT‐GFP or Ad‐ATP7BH1069Q‐GFP and incubated with p38 or JNK inhibitor. CuSO4 at 100 μM concentration was added to the cells for the last 2 hours of incubation with the inhibitors. The cells were examined by ICP‐MS (see Materials and Methods), which revealed an increase in normalized intracellular Cu levels (average ± standard deviation, n = 3 experiments) in ATP7BH1069Q‐expressing cells. Both p38 and JNK inhibitors reduced Cu levels in ATP7BH1069Q‐expressing cells. (B) HepG2 cells were infected with Ad‐ATP7BWT‐GFP or Ad‐ATP7BH1069Q‐GFP, incubated for 2 hours with 100 μM CuSO4, and loaded with CS3 before fixation. p38 or JNK inhibitors were added to the cells 24 hours before fixation (as indicated in the corresponding panels). Confocal microscopic images show CS3 fluorescence in red (top row), in white (middle row), and in false color scale (bottom row). Cells expressing ATP7BH1069Q exhibited higher CS3 signals than cells expressing ATP7BWT, while both p38 and JNK inhibitors decreased CS3 fluorescence in ATP7BH1069Q‐expressing cells. (C) Quantification revealed an increase in CS3 fluorescence (average ± standard deviation, n = 10 fields) in cells expressing ATP7BH1069Q and a decrease of CS3 signal upon incubation with either p38 or JNK inhibitor. Scale bar = 14 μm (C). Abbreviations: AU, arbitrary units; inh, inhibitor; WT, wild type.
