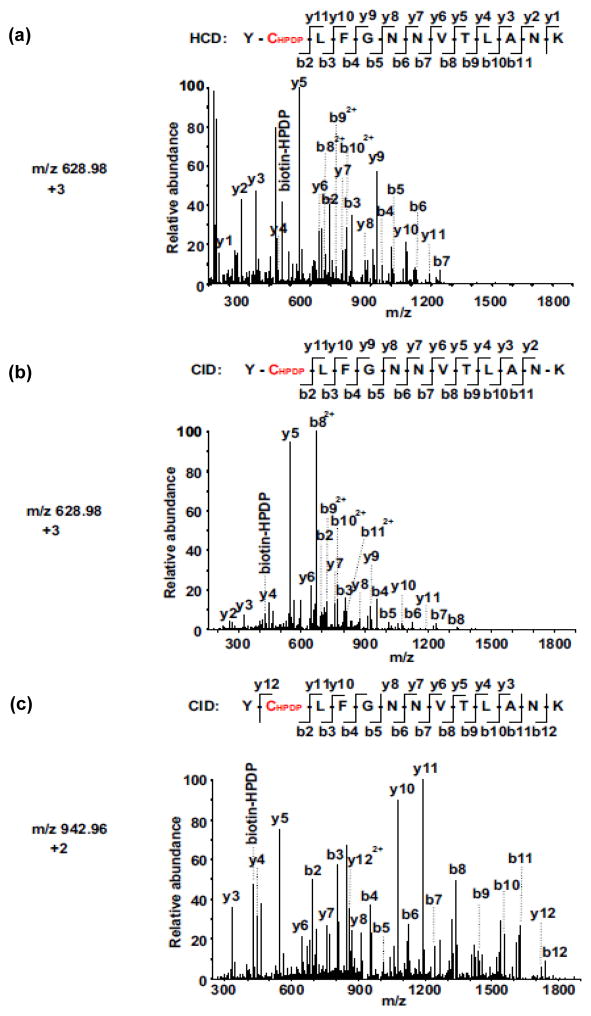
Fig. 2. Comparison of CID vs. HCD MS/MS spectra for the identification of biotinylated-Cys594 in YCLFGNNVTLANK of sGC α subunit.
(a) HCD MS/MS spectrum of the triply-charged biotinylated-peptide ion at m/z 628.97. (b) CID MS/MS spectrum of the triply-charged biotinylated-peptide ion at m/z 628.98. (c) CID MS/MS spectrum of the doubly-charged biotinylated-peptide ion at m/z 942.96. The SNO-Cys site was located on Cys594 in sGC α subunit. Both spectra (a and b) contain almost complete series of the y+ and b+ ions with the biotinylated-Cys (+428.19 at Cys) found between b1 and b2, as well as between y11 and y12 ions. The MS/MS fragmentation of the doubly-charged biotinylated-peptide ion was not observed by HCD mode. More y+ ions were observed from the HCD spectrum compared to the CID spectrum, due to the superior capability of HCD to detect low mass fragments.