Fig 2. Histologic Features of HPV-Associated OPSCC and HPV Status.
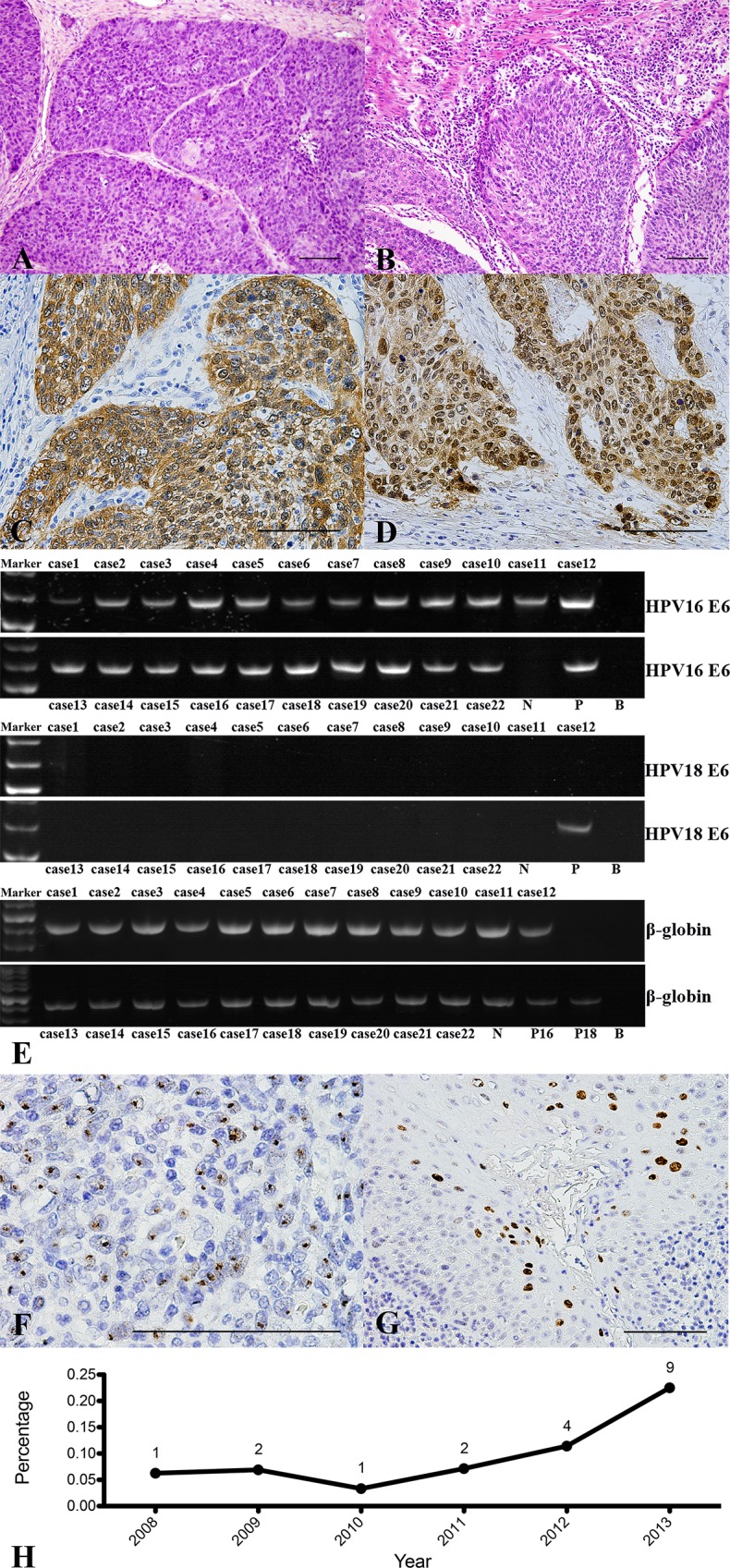
(A, B) HE staining of HPV-associated OPSCC with poorly differentiated tumor epithelial nests and a large number of lymphocytic infiltrations (200×). (C, D) Strong diffuse brown signals showing p16INK4A expression in the tumor cell plasma and nuclei by immunohistochemistry in ≥70% of malignant cells. (E) Native PAGE results for HPV16/18 E6: N, negative; P, positive; B, Blank; P16, HPV16 positive control; P18, HPV18 positive control. (F) 1000× magnification (hybridization dots within tumor cell nuclei, inset), integrated form. (G) 400× magnification (diffuse hybridization signals within tumor cell nuclei, inset), episomal form. (H) The proportion of HPV16-associated OPSCC/OPSCC cases from 2008 to 2013.
