Figure 1.
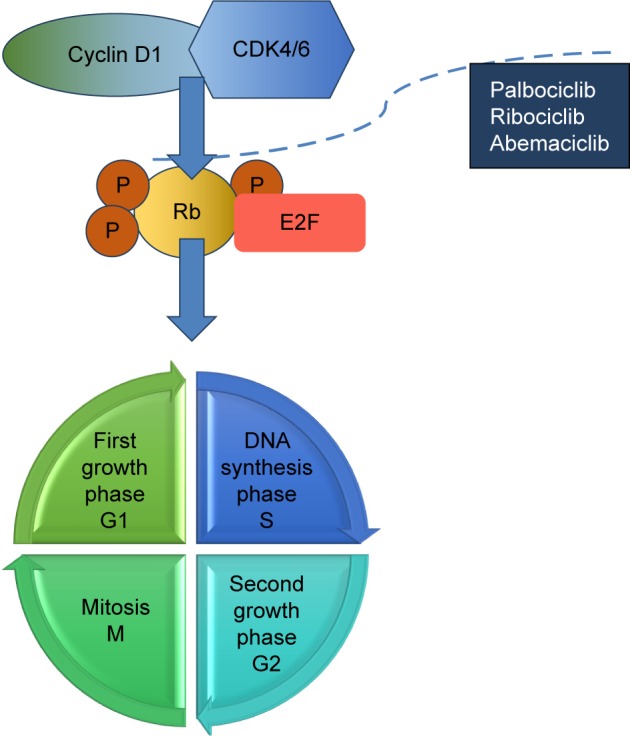
CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors mechanism of action.
Notes: In ER+ve/HER2−ve breast cancer oncogenic signals promote expression of cyclin D1 and activate CDK4/CDK6, which could result in breast-cancer proliferation. Cyclin D1 forms activating complexes with CDK4/6, which initiate pRb. In the presence of hyperphosphoryated pRb, the E2F is released and the cell cycle goes through S phase. Small molecule kinase inhibitors of CDK4/6 (palbociclib, ribociclib, abemaciclib) block the hyperphosphorylation of pRb and induce G1 cell arrest.7
Abbreviations: CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; E2F, transcription factor E2; ER, estrogen receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor 2; Rb, retinoblastoma; pRb, Retinoblastoma protein; P, phosphate.
