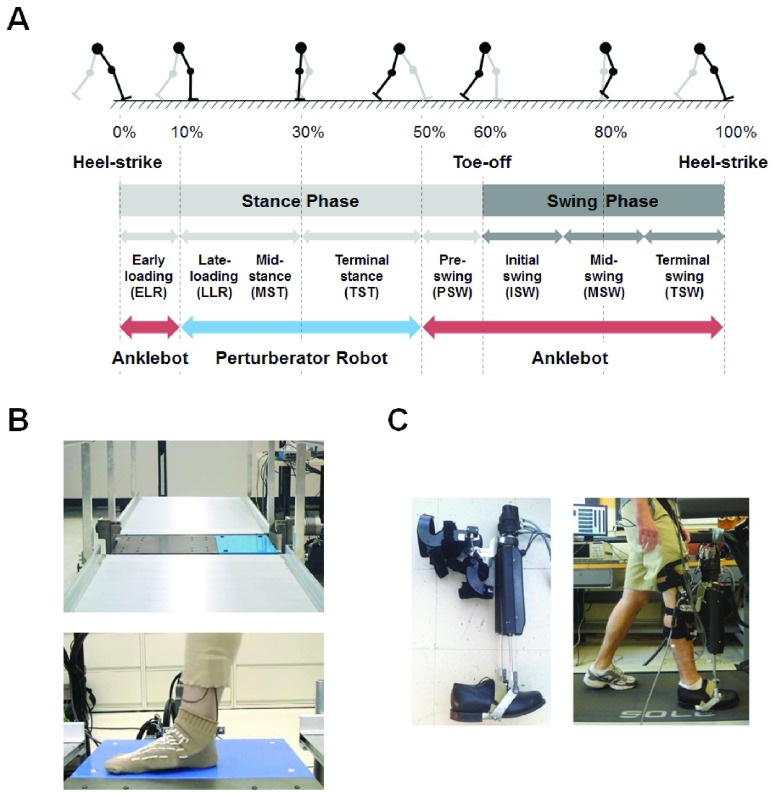
FIGURE 1.
Two robotic platforms to estimate ankle impedance during walking. A: From late-loading response to terminal stance phase, i.e, when the foot was flat to the ground, ankle impedance was estimated by a mechatronic platform, recessed into a walkway (B). From pre-swing phase through the entire swing phase to early-loading response, i.e, when the toe and/or heel were off the ground, ankle impedance was estimated by a wearable ankle robot (C). B: The Perturberator robot was comprised of a force platform coupled to a gear-motor that was controlled by a servodrive and microcontroller. C: The Anklebot was mounted onto the knee brace and its end-effectors were connected to a rigid U-shaped bracket attached to the bottom of a shoe (left). The robot was properly attached to the subjects’ right leg, and subjects were instructed to walk on a treadmill with the robot (right).