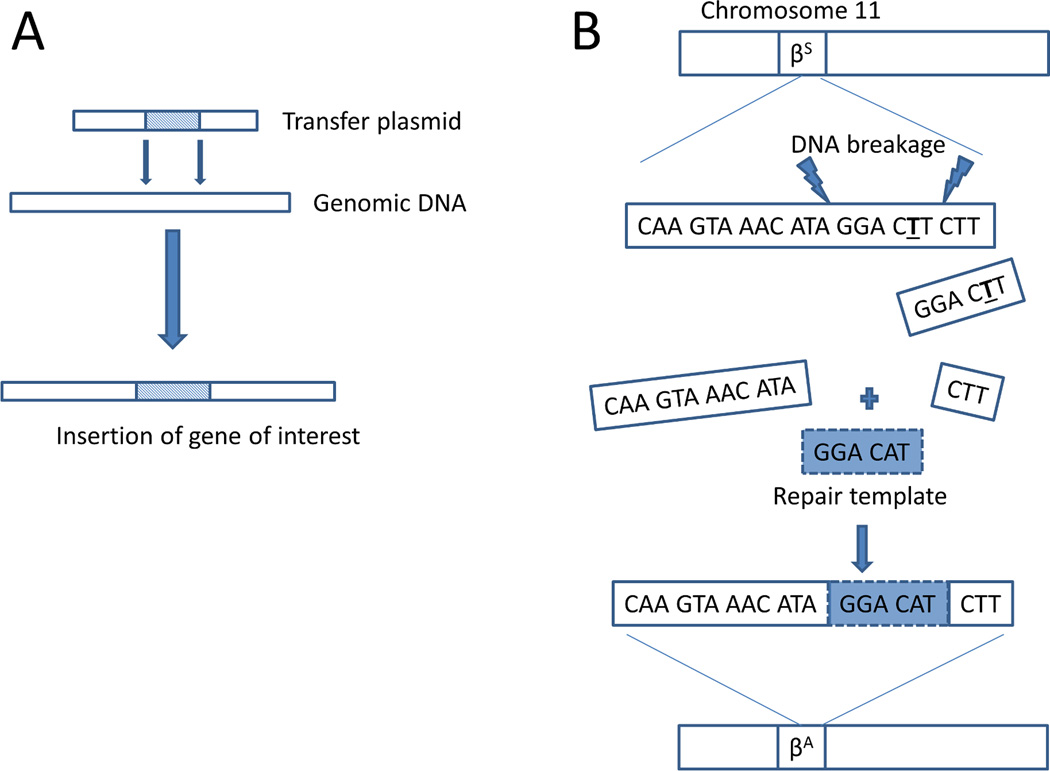
Figure 1. Curative gene therapy strategies for Sickle Cell Disease.
(A) Gene transfer or gene addition approaches involve a transfer vector (lentiviral, retroviral, transposon) that introduces a globin gene (gamma globin, beta globin, anti-sickling beta globin mutant) into random sites in genomic DNA in hematopoietic stem cells. The transferred globin competes with sickle beta globin for alpha globin to form normal hemoglobin molecules leading to disease resolution (B) Gene editing or correction strategies involve inducing DNA breaks (Zinc finger nuclease, CRISPR/Cas9. TALEN) in the mutated sickle beta globin gene and providing a repair template with the normal DNA sequence to be used in the cell’s DNA repair mechanism.