Figure 6. Unexpected contamination provides a signature developmental impact and transcriptional response for a brominated diphenyl ether.
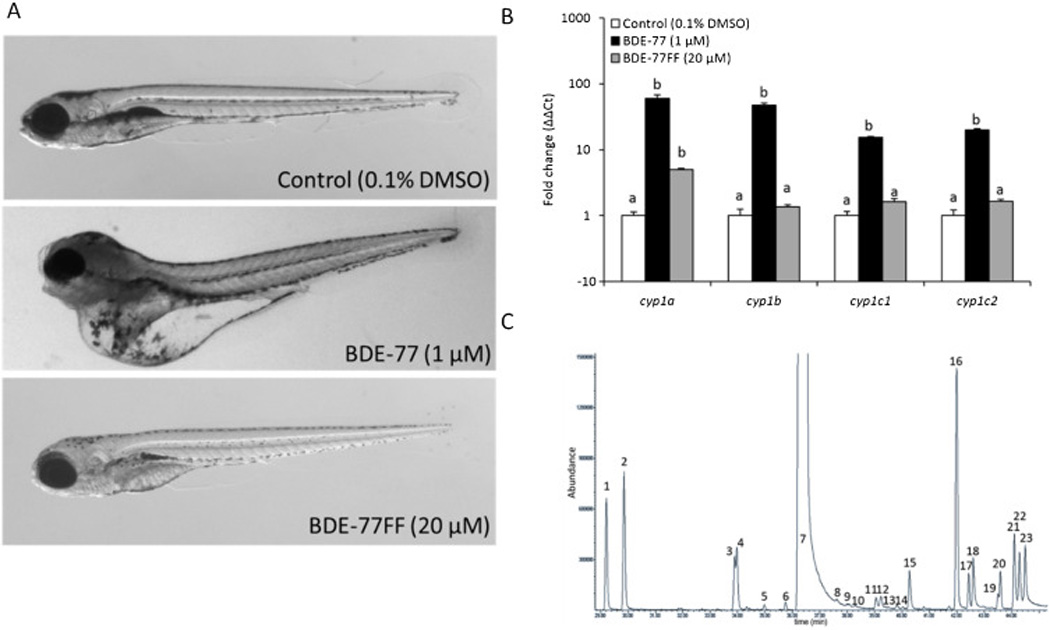
(A) Example photomicrographs of 120 hpf embryos exposed to Control (0.1% DMSO), BDE-77 (1 µM), and BDE-77FF (20 µM; BDE-77 preparation further purified to remove dioxin/furan contamination). (B) Whole animal expression of AHR-dependent cytochrome P450 genes (cyp1a, cyp1b, cyp1c1, cyp1c2) was analyzed in 120 hpf animals treated from 6–8 hpf to 120 hpf with either the EC100 for BDE-77 (1 µM), or highest concentration tested for BDE-77FF (20 µM). Bars not labelled with the same letter were significantly different (ANOVA on ranks, Student-Newman-Keuls, p ≤ 0.05, N = 4 replicates with 12 animals each). (C) Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis for BDE-77 shows a complex mixture of over twenty low level contaminant compounds present in the BDE lot that elicited developmental toxicity.
