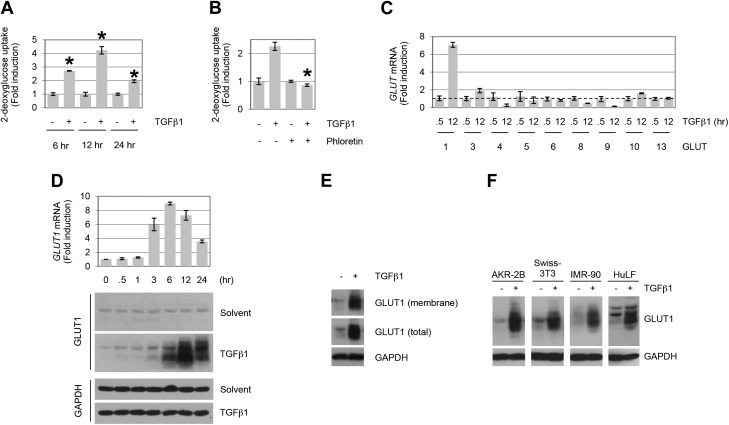
Figure 1.
TGF-β stimulates GLUT1 up-regulation and glucose uptake in fibroblasts. A) AKR-2B cells were treated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml), and 2-deoxyglucose uptake was determined at the indicated times (n = 3). B) Glucose uptake assay in TGF-β1–treated (12 h) AKR-2B fibroblast cells. Results show an increase in 2-deoxyglucose uptake, which is inhibited by the GLUT-specific inhibitor, phloretin (100 μM; n = 3). C) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses of GLUT induction by TGF-β1 in AKR-2B cells (n = 3). GLUT7 expression was not examined, whereas GLUTs 2 and 12 displayed no detectable expression. Dotted line indicates 1 unit on y axis. GLUTs 11 and 14 were not included, as no corresponding murine genes have been reported. The profiles of GLUT expression indicate that GLUT1 and GLUT3 exhibit >2-fold induction by TGF-β1, although only GLUT1 protein showed a parallel increase (data not shown for GLUT3 protein). D) AKR-2B cells were treated for the indicated times with TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) or solvent (4 mM HCl, 1.0 mg/ml bovine serum albumin), and at the indicated times whole-cell lysates were prepared for quantitative PCR (top) or Western blot analysis (bottom) and blotted for GLUT1 or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Data show a time-dependent up-regulation of GLUT1 mRNA and protein by TGF-β1 (n = 3). E) Subcellular localization of GLUT1 in AKR-2B fibroblasts. Cell-surface biotinylation reveals the presence of GLUT1 in the membrane fraction under basal and TGF-β–stimulated (12 h) conditions. F) Profiles of GLUT1 protein expression in human (IMR-90 and HuLF) and murine (AKR-2B and Swiss-3T3) fibroblasts stimulated with TGF-β1 (18 or 24 h for HuLF). Results demonstrate that TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) triggers GLUT1 up-regulation in various fibroblast cells. Asterisks denote statistical significance. Supplemental Tables 2 and 3 provide P values for indicated data points.