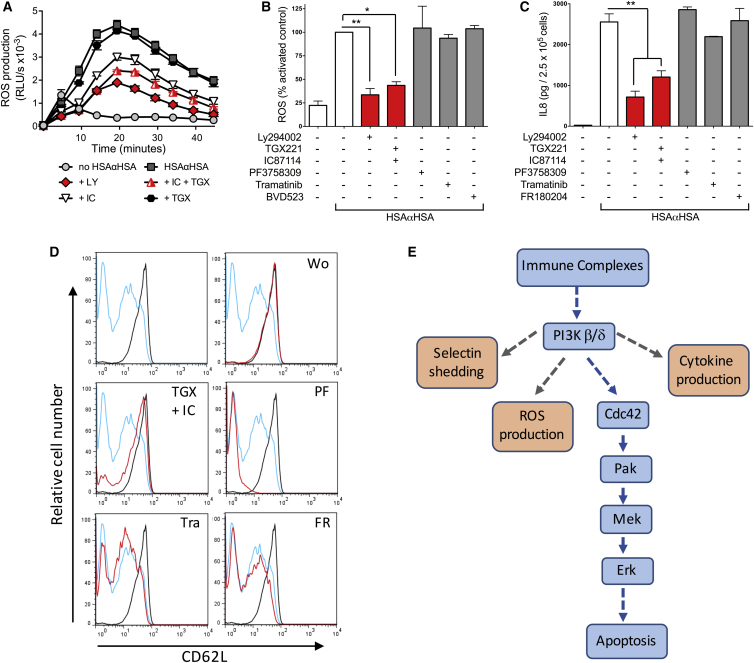
Figure 7.
PI3Kβ/δ Signaling Regulates iIC-Induced Neutrophil Functions Other Than Apoptosis
Peripheral blood-derived healthy donor neutrophils were pre-incubated with small-molecule inhibitors (LY294002, stable pan-PI3K inhibitor; TGX221, PI3Kβ; IC87114, PI3Kδ; PF3758309, Pak; tramatinib, Mek; FR180204 and BVD523, Erk) or vehicle at 37°C for 10 min as indicated prior to stimulation with 10 μg/mL iIC.
(A and B) Characterization of iIC-induced internal ROS production.
(A) The data (mean ± range) presented are from a representative experiment employing PI3K inhibitors of a total of three performed.
(B) Total light emissions (mean ± SEM) of inhibitor-treated cells expressed as percentage of the response obtained with stimulated control cells. Data were pooled from a minimum of three separately conducted experiments.
(C) Cells were cultured for 12 hr, followed by analysis of cytokine release in the culture supernatants by ELISA. The data shown were pooled from three separately conducted experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(D) Neutrophil surface CD62L was analyzed by flow cytometry. For ease of viewing, the mock-stimulated and iIC-stimulated histograms were copied into each inhibitor treatment (black, basal cells; blue, iIC-stimulated cells; red, iIC-stimulated and inhibitor-treated cells). A representative experiment is presented from a total of three separate experiments performed.
(E) A schematic of the non-canonical signaling pathway regulating apoptosis in iIC-stimulated human neutrophils (blue boxes). This unusual pathway regulates Mek and Erk independently of Ras and Raf, instead using Cdc42 and Pak to regulate iIC-induced neutrophil apoptosis. Other functions are regulated by PI3Kβ/δ employing diverging pathways (orange boxes).
See also Figure S4.