Figure 4.
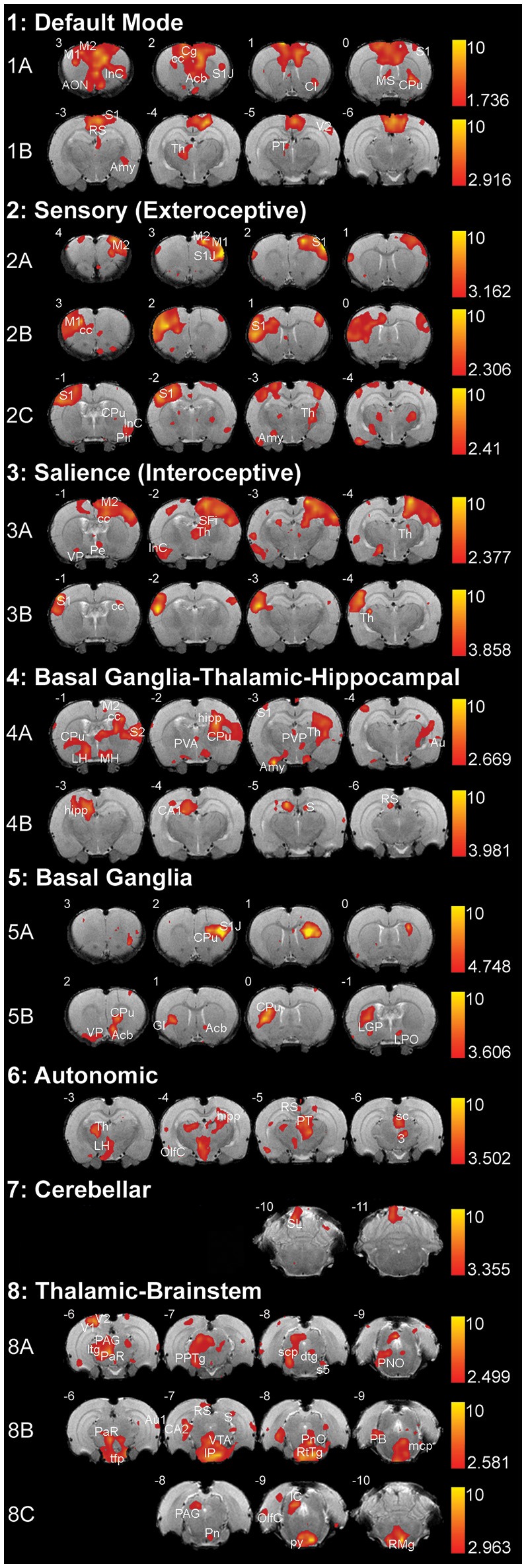
Resting-state networks in 2-week-old rats. The figure illustrates eight different resting-state networks that were identified in 2-week-old rats (N = 11; 5 female and 6 male from 4 different litters) under light anesthesia. Networks 1–7 showed some spatial similarity to adult networks and included: (1) Default Mode Network, (2) Sensory (Exteroceptive) Network, and (3) Salience (Interoceptive) Network, (4) Basal Ganglia-Thalamic-Hippocampal Network, (5) Basal Ganglia, (6) Autonomic, and (7) Cerebellar Network. The last, (8) Thalamic-Brainstem Network has not been described in adult rats. With the exception of Autonomic and Cerebellar Networks, all others were comprised of multiple components extracted by Melodic. The resting-state networks maps are represented as z-scores. The threshold bars show a maximum threshold of 10 and the minimum z-score necessary for significance for each component. The positive map colors range from dark red to yellow. The numbers in the upper left corner of each coronal section refer to distance from Bregma (mm). Each individual coronal section corresponds to traditional radiographic orientation; the left hemisphere of the brain corresponds to the right side of the image. Anatomical abbreviations were adopted from Rat Brain Atlas (Paxinos and Watson, 1998). 3, oculomotor nucleus; Acb, accumbens nucleus; Amy, amygdala; AON, anterior olfactory nucleus; Au1, primary auditory cortex; Au, auditory cortex; CA1; field CA1 of hippocampus; CA2; field CA2 of hippocampus; Cb6, cerebellar lobule 06; Cb7, cerebellar lobule 07; Cb8, cerebellar lobule 08; cc; corpus callosum; Cg, cingulate cortex; Cl, claustrum; CPu, caudate putamen; dtg, dorsal tegmental bundle; GI, granular insular cortex; hipp, hippocampus; ic, internal capsule; IC, inferior colliculus; IP, interpeduncular nucleus; InC, insular cortex; LGP, lateral globus pallidus; LH, lateral hypothalamus; LPO, lateral preoptic area; M1, primary motor cortex; M2, secondary motor cortex; mcp, medial cerebellar peduncle; MH, medial hypothalamus; MS, medial septal nuclei; OlfC, olfactory cortex; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PaR, pararubral nucleus; PB, parabrachial nucleus; Pe, periventricular hypothalamic nucleus; Pir, piriform cortex; PnO, pontine reticular nucleus, oral part; PPTg, pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus; PT, pretectum; PVA, paraventricular thalamic nucleus—anterior; PVP, paraventricular thalamic nucleus; py, pyramidal tract; RS, retrospenial cortex; RtTg, reticular tegmentum; S, subiculum; S1, primary somatosensory cortex; S1J, primary somatosensory cortex—jaw region; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex; s5, sensory root of trigeminal nucleus; sc, superior colliculus; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle; SFi, septofimbrial nucleus; tfp, transverse fibers of pons; Th, thalamus; V1, primary visual cortex; V2, secondary visual cortex; VP, ventral pallidum; VTA, ventral tegmental area.
