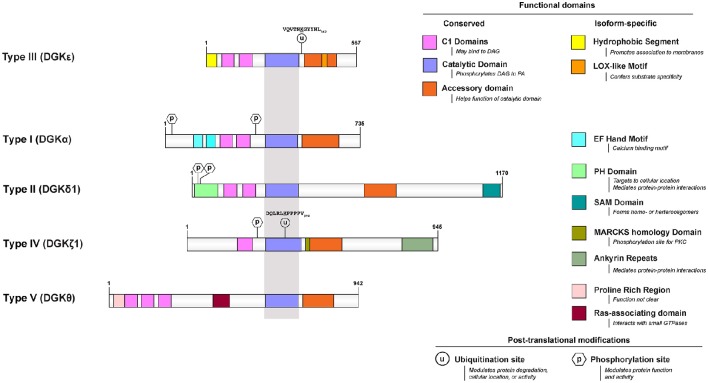
Figure 1.
Functional domains of DGKε are contrasted to that of prototypical DGKs from the other 4 subtypes. All protein models were drawn to scale using the Illustrator for Biological Sequences (http://ibs.biocuckoo.org/) (Liu et al., 2015). The proteins are centered around the shared catalytic site (grayed area) because it is the most conserved feature across subtypes. Features that are unique to DGKε and other DGKs are listed on the right side. Known and/or possible phosphorylation (Shirai et al., 2012; Mertins et al., 2013; Park et al., 2015) and ubiquitination (Wagner et al., 2011; Komander and Rape, 2012; Mertins et al., 2013) sites are also displayed (see text and Table 1 for details). If there are more than one documented isoform, the characteristics of isoform 1 were used for each protein. The accession (and GI) numbers for the proteins illustrated are: DGKε, NP_003638.1 (4503313); DGKα, NP_958853.1 (41872494); DGK δ1, NP_003639.2 (25777596); DGKθ, NP_001338.2 (40806175); DGKζ1, NP_963290.1 (41872522).