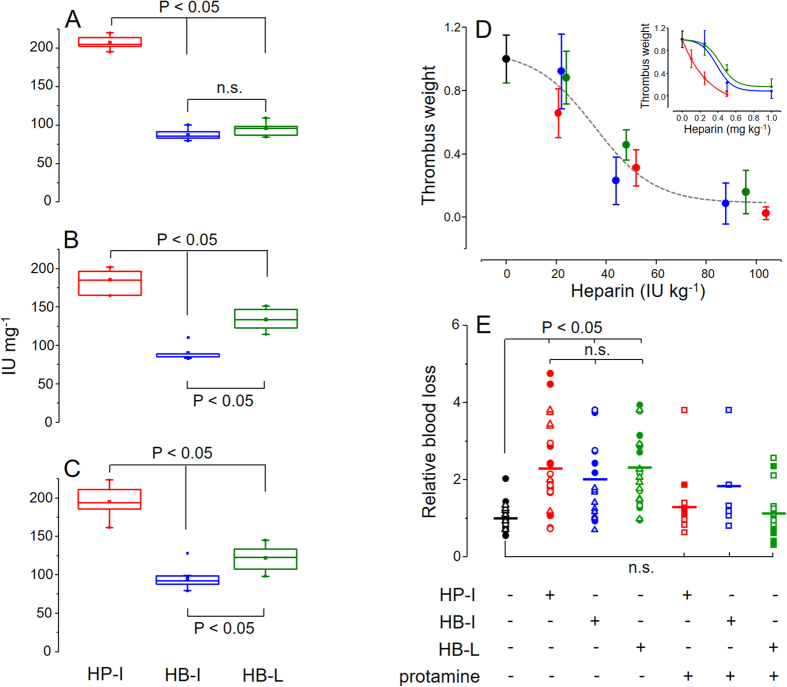
Figure 5. In vitro anticoagulant and in vivo antithrombotic and bleeding effects of heparins from different animal sources.
HP-I (in red), HB-I (in blue) and HB-L (in green) were evaluated in vitro on APTT (A), anti-FIIa (B) and anti-FXa (C) and in vivo on venous thrombosis (D) and bleeding tendency (E) assays. Data from the in vitro assays (panels A–C) were expressed as median (CI 95%) and mean (□) and compared via One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. The anticoagulant activities (IU mg−1, as dry weight) were determined based on standard curves obtained with the 6th International Heparin Standard (NBISC). In vivo antithrombotic activities (normalized results) were expressed as IU kg−1 body weight (a single sigmoidal curve for the three heparin types) in panel D and as mg kg−1 body weight in panel D inset (mean ± SD, n ≥ 5). Bleeding tendencies (panel E) were expressed as ratios of blood loss of animals treated with the heparins (200 IU kg−1 body weight) and saline (control, in black). In part of the assays heparins were neutralized with 2 mg kg−1 body weight of protamine before the bleeding measurement. Full and empty squares, circles and triangles represent different experimentalists.