Figure 1.
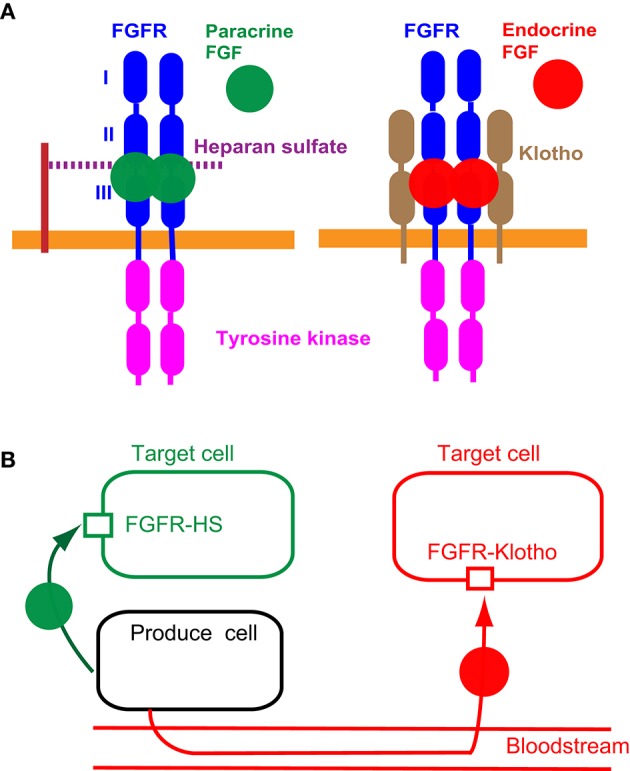
Mechanisms of action of paracrine and endocrine FGFs. (A) Paracrine FGFs specifically bind to the FGFR-heparan sulfate complex and activate FGFR tyrosine kinase. Endocrine FGFs specifically bind to the FGFR-Klotho complex and activate tyrosine kinase. This, in turn, induces the activation of intracellular pathways (Ornitz and Itoh, 2015; Brewer et al., 2016). (B) Paracrine FGFs are secreted local signals that act on nearby target cells by diffusion with functions in multiple developmental and pathophysiological processes. Endocrine FGFs are secreted endocrine signals that act on distant target cells through the bloodstream with multiple functions in metabolic and pathophysiological processes. FGFR-HS and FGFR-Klotho indicate the FGFR-heparan sulfate complex and FGFR-Klotho complex, respectively (Ornitz and Itoh, 2015; Brewer et al., 2016).
