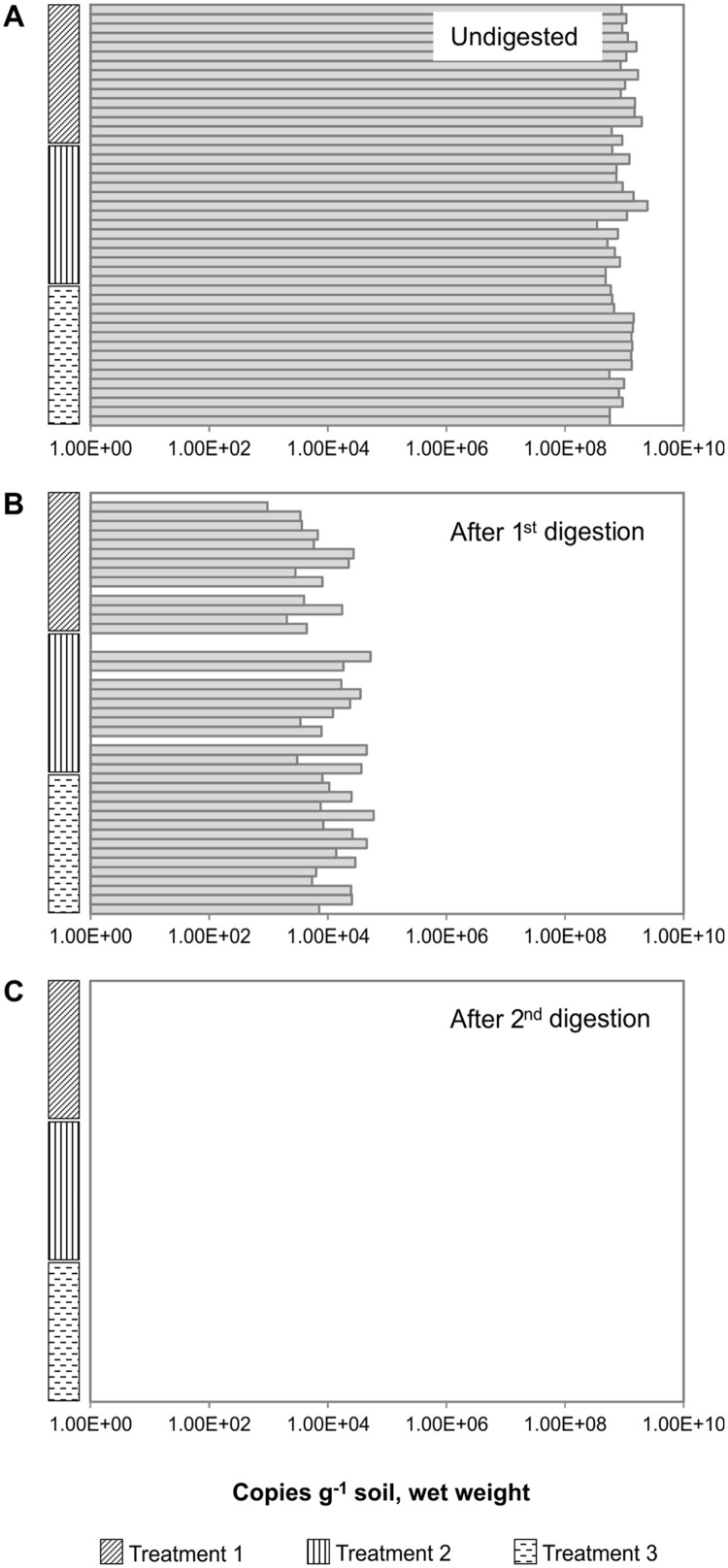
FIGURE 3.
Removal of gDNA by consecutive DNase digestions of total nucleic acids (TNA) extracted from 45 Å soil samples. The soil had been exposed to different oxygen regimes (here called Treatments 1, 2, and 3), for details see section “Materials and Methods.” The soils were incubated anoxically to stimulate denitrification gene expression, and samples were taken at time intervals. TNA was extracted using the optimized and simplified method, and the nosZ was quantified by qPCR. (A) After extraction via the optimized method, all samples were tested for the presence of DNA. Neither the different oxygen regimes nor the stimulation of gene expression affected the number of nosZ genes in the gDNA from the different samples. (B) The first digest removed most amplifiable genomic DNA (gDNA) present. (C) The second DNase treatment removed amplifiable gDNA in all samples. There was no relationship between the starting DNA quantity and the success of complete gDNA removal (R2 = 0.0189). This highlights the importance of checking all RNA samples and not only representative samples, as there may be high variability among samples from the same source and extraction procedure.