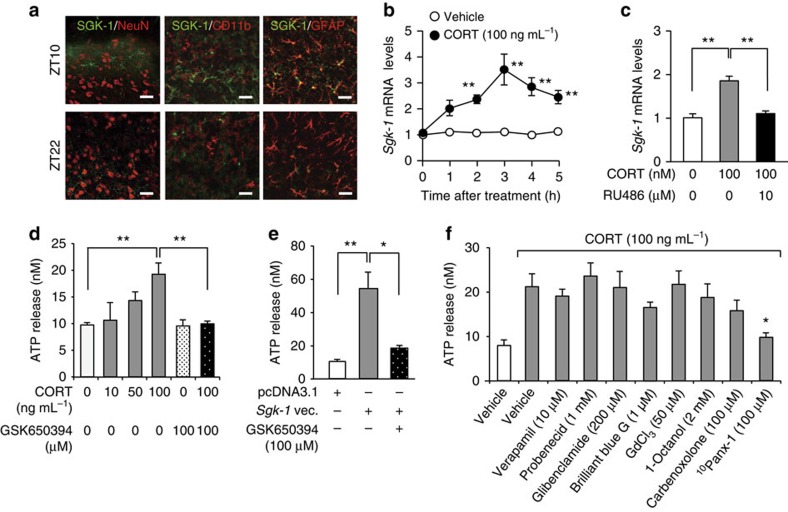
Figure 5. The expression of SGK-1 enhances ATP release from astrocytes.
(a) Double immunofluorescence labelling of SGK-1 with NeuN, a marker of neurons; CD11b, a marker of microglia; and GFAP, a marker of astrocytes in the ipsilateral spinal slices of male sham+PSL mice at ZT10 and ZT22. SGK-1-positive cells are double-labelled (yellow) with GFAP at ZT10. This experiment was performed on day 7 after nerve injury. Scale bar, 10 μm. Data are representative of five independent experiments. (b) Time course of the CORT-induced expression of Sgk-1 mRNA in primary cultures of astrocytes (means±s.e.m.; n=5). **P<0.01 significantly different from the basal level (F11,48=25.460, P<0.001, ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer's PHT). (c) The induction of Sgk-1 mRNA by CORT (100 ng ml−1) is inhibited by 10 μM RU486 (means±s.e.m.; n=5). **P<0.01 significant difference between two groups (F2,12=55.500, P<0.001, ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer's PHT). (d) The SGK-1 inhibitor GSK650394 prevents the CORT-induced release of ATP from primary cultured astrocytes (means±s.e.m.; n=5). Cells were treated with CORT for 4 h in the presence or absence of 100 μM GSK650394. **P<0.01 significant difference between two groups (F5,24=6.175, P=0.017, ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer's PHT). (e) GSK650394 prevents the SGK-1-induced release of ATP from primary cultured astrocytes (means±s.e.m.; n=5). Sgk-1-expressing vector-transfected astrocytes were incubated in the presence or absence of 100 μM GSK650394. **P<0.01, *P<0.05 significant difference between two groups (F2,12=13.508, P=0.002, ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer's PHT). (f) Effects of inhibitors on candidate pathways for the CORT-induced release of ATP from astrocytes (means±s.e.m.; n=5–6 per group). Cells were treated with CORT for 4 h in the presence or absence of each inhibitor. *P<0.05 significant difference from CORT alone-treated cells (F9,45=3.094, P=0.005, ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer's PHT).