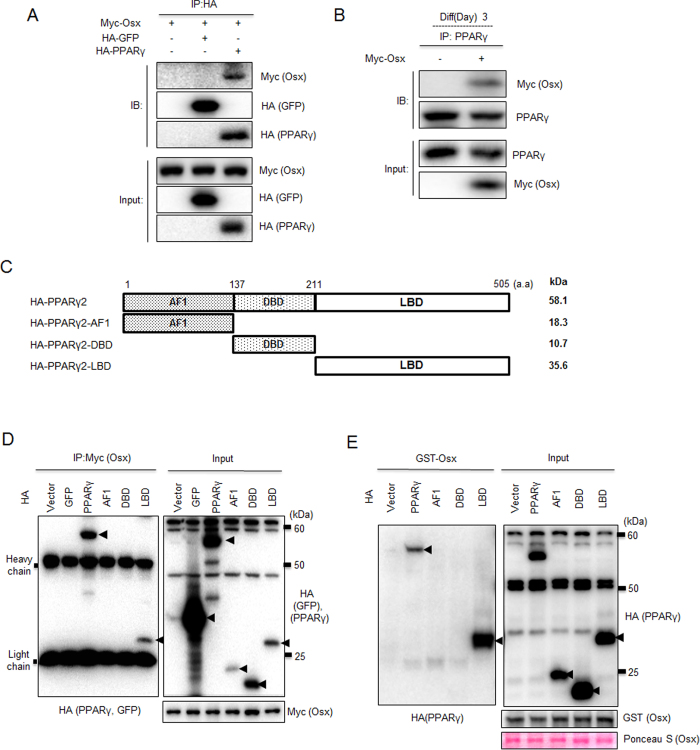
Figure 5. The LBD of PPARγ is involved in the interaction with Osterix.
(A) 3T3-L1 cells were transfected with indicated expression plasmids. To examine the binding of Osterix and PPARγ, whole cell extracts were prepared and co-immnunoprecipitation was performed using HA antibody with subsequent western blotting using Myc or HA antibodies. (B) 3T3-L1 cells were transfected with Myc-Osterix plasmid or empty Myc vector. Cells were then cultured in MDI-containing differentiation medium for 3 days. The interaction between endogenous PPARγ and overexpressed Osterix is examined by IP using a PPARγ antibody followed by IB using a Myc antibody. (C) To identify the PPARγ domain that interacts with Osterix, a deletion construct of PPARγ was constructed. A depiction of the construct is shown here. (D) 3T3-L1 cells were transfected with indicated expression plasmids. To examine the binding of Osterix to the AF1, DBD, and LBD of PPARγ, co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed using a Myc antibody and western blotting was performed with Myc or HA antibodies. (E) Identification of the PPARγ domain that interacts with Osterix in vitro. The purified HA-tagged PPARγ deletion constructs were incubated with GST-Osx in separate incubation reactions and the bound proteins were identified by western blot analysis. Additionally, expression of GST proteins was confirmed by Ponceau S staining.