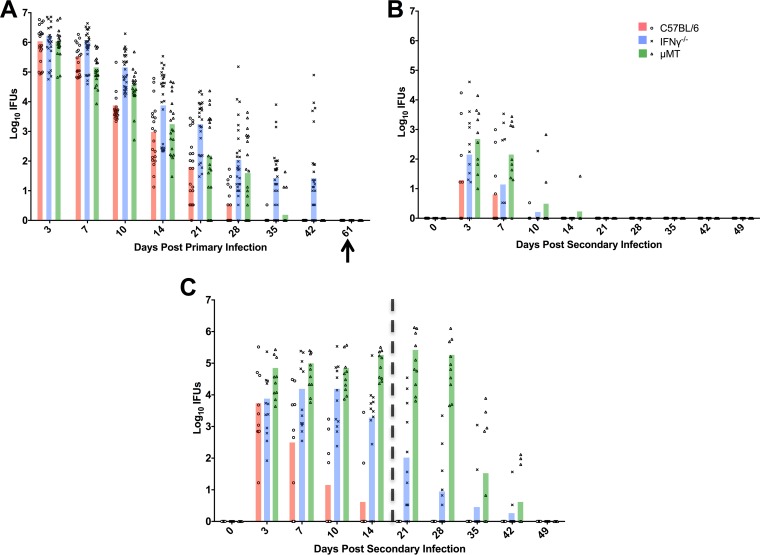
FIG 3.
Effect of IFN-γ on bacterial clearance during primary and secondary C. muridarum infection. Shedding of chlamydiae was determined by quantitating IFUs from cervicovaginal swabs collected at various times following infection. (A) Infection course of primary infection in C57BL/6 mice (n = 20), IFN-γ−/− mice (n = 32), and μMT mice (n = 20). The arrow indicates a negative cervicovaginal culture following the conclusion of antibiotic treatment. Half of the mice of each strain (among those described for panel A) were depleted of CD4+ T cells as described in Fig. 1, and all mice (including the CD4-depleted and nondepleted mice) were rechallenged with C. muridarum 66 days following primary infection. (B and C) Course of secondary rechallenge infection in nondepleted (B) and CD4-depleted (C) mice. The vertical dashed line at day 20 in panel C represents the last dose of anti-CD4 treatment. Data are presented as IFUs from two independent experiments. Statistical comparisons are listed below rather than on the figures for clarity. For primary infection, statistical significance was determined as follows: for C57BL/6 versus IFN-γ−/−, P < 0.0001 for days 10 through 42; for IFN-γ−/− versus μMT, P < 0.05 for day 7, P < 0.01 for day 21, and P < 0.0001 for days 35 and 42; for C57BL/6 versus μMT, P < 0.05 for day 10 and P < 0.0001 for day 28. For nondepleted secondary infection, statistical significance was determined as follows: for C57BL/6 versus IFN-γ−/−, P < 0.01 for day 3; for IFN-γ−/− versus μMT, P < 0.001 for day 7; for C57BL/6 versus μMT, P < 0.0001 for days 3 and 7. For CD4-depleted secondary infection, statistical significance was determined as follows: for C57BL/6 versus IFN-γ−/−, P = 0.0001 for day 7 and P < 0.0001 for days 10, 14, and 21; for IFN-γ−/− versus μMT, P < 0.0001 for days 14, 21, and 28; for C57BL/6 versus μMT, P < 0.05 for day 3, P < 0.0001 for days 7 through 28, and P < 0.01 for day 35.