Table 1.
Structures and major characteristics of MAO inhibitors mentioned in the text.
| Compound | Activity | Status | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenelzine | Irreversible MAO-A + MAO-B | Used as antidepressant Hepatotoxicity Needs dietary control for restriction of tyramine intake | 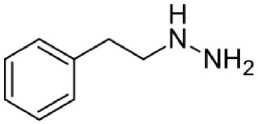 |
| Tranylcypromine | Irreversible MAO-A + MAO-B | Used as antidepressant with dietary control | 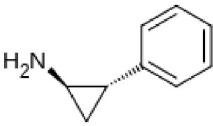 |
| Pargyline | Irreversible MAO-A and MAO-B | Antidepressant and antihypertensive Currently not in clinical use | 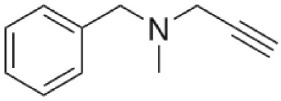 |
| Selegiline | Irreversible MAO-B selective (R- enantiomer) Selectivity is dose dependent in vivo | Metabolism to amphetamines | 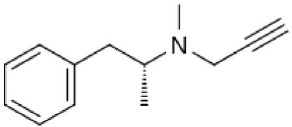 |
| Clorgyline | Irreversible highly MAO-A selective | Antidepressant effect demonstrated in humans but not in clinical use | 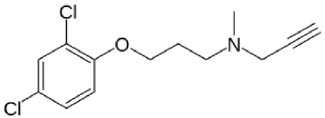 |
| Moclobemide | Reversible highly MAO-A selective | Moderately effective antidepressant drug | 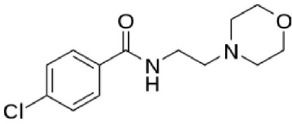 |
| Rasagiline | Irreversible MAO-B selective (R+ enantiomer) Selectivity is dose dependent in vivo | Neuroprotective in vitro, anti-Parkinson drug, metabolism to 1-aminoindan | 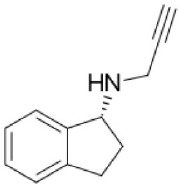 |
| Safinamide | Reversible highly MAO-B selective | Anti-Parkinson drug, glutamate receptor antagonistic and Na+ channel blocking properties | 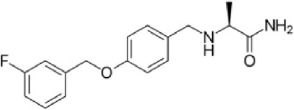 |
| Ladostigil | MAO-A + MAO-B Relative brain selectivity, minimal tyramine potentiation | Cholinesterase and MAO inhibition | 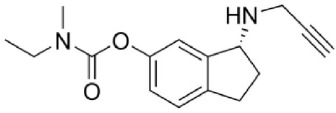 |
| VAR 10303 | MAO-A + MAO-B Relative brain selectivity, minimal tyramine potentiation | Fe chelation and MAO inhibition | 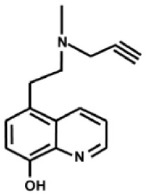 |
| M30 | MAO-A and MAO-B Relative brain selectivity | Fe chelation and MAO inhibition | 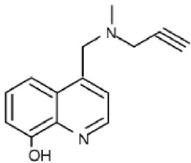 |
