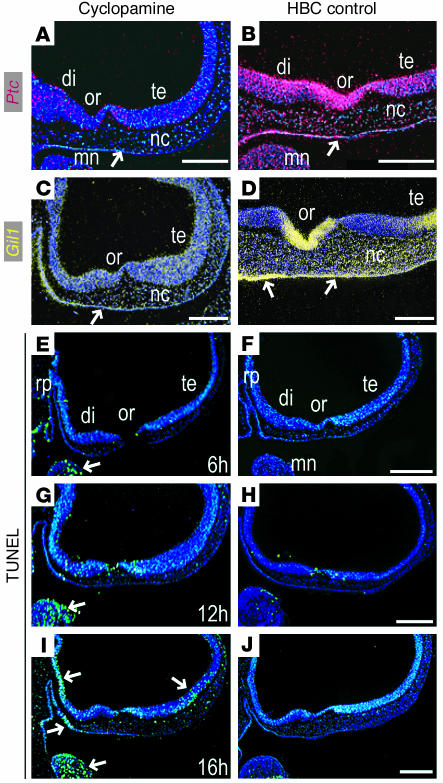
Figure 5.
Cyclopamine blocks Shh signal transduction in the craniofacial complex. (A) Within 16 hours of cyclopamine exposure at St. 17, Ptc is downregulated in the diencephalic (di) and telencephalic (te) neuroectoderm, in frontonasal mesenchyme, and in facial ectoderm (arrow) relative to HBC controls (B). (C) Gli1 is similarly downregulated in the craniofacial tissues compared with HBC controls (D). (E–J) Despite these molecular changes, few cells within the frontonasal primordium undergo programmed cell death. (E) Within 6 hours of cyclopamine treatment, there is little evidence of DNA fragmentation in the craniofacial region, as indicated by TUNEL staining (arrow); compare with HBC control embryos (F). (G) Within 12 hours of treatment, few if any TUNEL-positive cells are detectable in the frontonasal primordium, although TUNEL staining in the mandible was increased relative to HBC-treated embryos (H). (I) Sixteen hours after treatment, TUNEL-positive staining is evident in diencephalic and telencephalic neuroectoderm and in ventral facial ectoderm (arrows) compared with HBC-treated controls (J). Scale bars: 200 μm.