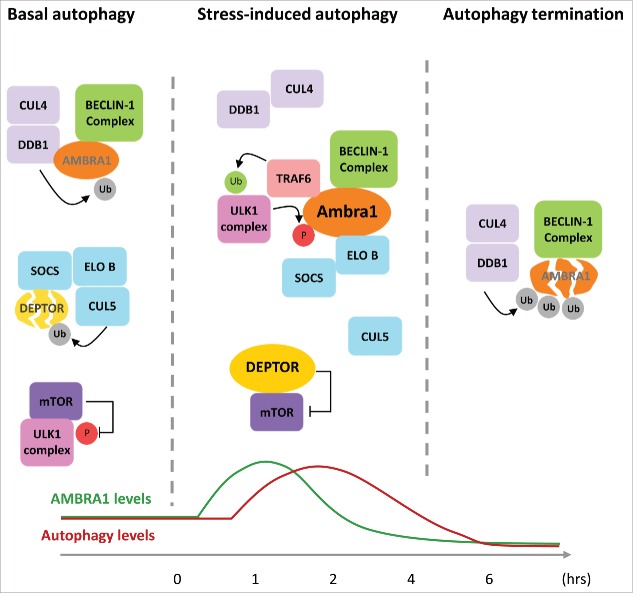
Figure 1.
Crosstalk between AMBRA1 and CULLIN E3 ubiquitin ligases regulates autophagy. In unstressed conditions, AMBRA1 protein levels are kept low by the DDB1/CULLIN 4 E3 ubiquitin ligase (CUL4) complex, ULK1 activity is repressed by mTOR, and DEPTOR protein is degraded by a CULLIN 5 (CUL5) complex containing ELONGIN B (ELO B) and a substrate receptor of the suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family. Autophagy stimuli rapidly lead to AMBRA1 protein stabilization by inducing AMBRA1-DDB1 dissociation in an ULK1-dependent manner. AMBRA1 is then able to interact with TRAF6 and activate ULK1 and BECLIN-1 complexes. Moreover, once free from CULLIN 4, AMBRA1 is able to inhibit the activity of the distinct E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, CULLIN 5, by interacting with its adaptor protein ELONGIN B. This leads to stabilization of the mTor inhibitor DEPTOR, which allows timely activation of ULK1 by decreasing the inhibitory phosphorylation mediated by mTOR. In prolonged stress conditions, CULLIN 4 re-associates with AMBRA1, causing rapid degradation and ending the autophagy response. Ub: Ubiquitin, P: Phosphorylation.